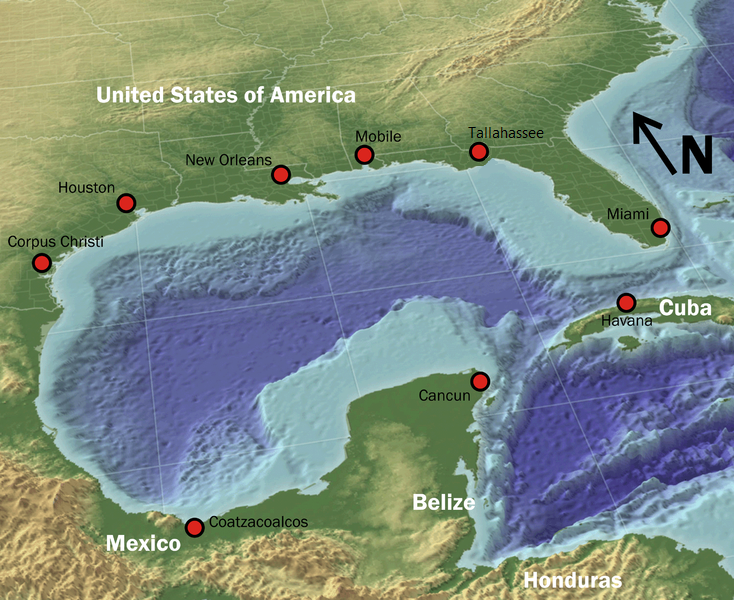
The Gulf of Mexico is the largest gulf in the world. The Gulf of Mexico (GOM) is a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean bordered by five states of the United States on the northern and the eastern border, five Mexican states on its western and southern border, and Cuba to the southeast.
The Gulf of Mexico is a major source of oil for the United States. In fact, it’s responsible for 54% of oil production in the U.S., and 47% of natural gas production. However, this does have a downside, such as the Deepwater Horizon oil spill in 2010 which poured an estimated 4.9 million barrels of oil in the Gulf.
The Gulf of Mexico consists of several ecological and geologic provinces, chief of which are the coastal zone, the continental shelf, the continental slope, and the abyssal plain. The coastal zone consists of tidal marshes, sandy beaches, mangrove-covered areas, and many bays, estuaries, and lagoons.
The Gulf of Mexico is recognized worldwide as a vast and productive body of water with tremendous value in ecological, economic, and social terms. The Gulf’s vastness and diversity often mask the fundamental relationships between the living and the non-living workings of the ecological system.
Can you swim in the Gulf of Mexico?
Yes, it is completely safe to swim in the Gulf of Mexico. Very rarely do we experience red tide or any other issues.
The Gulf continues to be the nation’s primary offshore source of oil and gas, generating about 97% of all U.S. OCS oil and gas production. The Gulf is a famous diving destination due to its large coral reefs. The Gulf is often portrayed as a hotspot for tourism, owing to the sprawling beaches along its coastline and the opportunity for recreational diving.
Why is the Gulf of Mexico not a sea?
Although the Gulf of Mexico is considered to be a part of the Atlantic Ocean, since an ocean has no boundaries, the Gulf and the Atlantic are still separated by the Caribbean Sea. In addition to their boundaries, there are numerous ways these two bodies of water vary and therefore, the beaches we enjoy are unique.
Why is the Gulf of Mexico rich in oil?
The main reason the Gulf of Mexico is such a hotbed for oil and gas exploration today is because it is stuffed full of so-called source rocks. These rocks were formed millions of years ago during the Cretaceous, pre-Cretaceous and Upper Jurassic eras, “when dinosaurs were out running around,” Roberts said.
Can alligators swim in the Gulf of Mexico?
While alligators can tolerate salt water for a few hours or even days, they are primarily freshwater animals, living in swampy areas, rivers, streams, lakes, and ponds.
What kind of animals live in Gulf of Mexico?
As one of the most staggeringly productive places on this planet, the Gulf is home to fish, coral, whales, sea turtles, dolphins and thousands of bird species.
How toxic is the Gulf of Mexico?
In the Gulf of Mexico, some harmful algal blooms are caused by the microscopic algae species Karenia brevis, commonly called red tide. These algal blooms can cause respiratory illness and eye irritation in humans. It can also kill marine life, and lead to shellfish closures.
What dangers are in the Gulf of Mexico?
Toxic algae, oil spills, severe weather, dangerous currents and coastal land loss are major threats to human health and safety in the Gulf. cause millions of dollars in tourism losses and send people with chronic respiratory diseases to emergency rooms.
