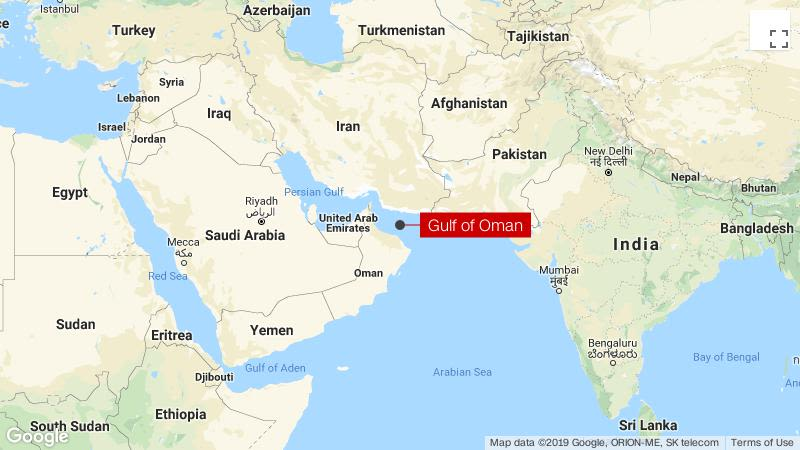
The Gulf of Oman or Sea of Oman (Arabic: خليج عمان khalīj ʿumān; Persian: دریای عمان daryâ-ye omân), also known as Gulf of Makran or Sea of Makran (Arabic: خلیج مکران khalīj makrān; Persian: دریای مکران daryâ-ye makrān), is a gulf that connects the Arabian Sea with the Strait of Hormuz, which then runs to the Persian Gulf. It borders Iran and Pakistan on the north, Oman on the south, and the United Arab Emirates on the west. 16. The Gulf of Oman is one of the important sea passages in Iran. It connects the Persian Gulf to the Indian Ocean. About half of the coastline of Iran is next to the Gulf of Oman and parts of it are considered as natural tourist sites of Iran.
The Gulf of Oman is about 320 km wide at its widest point between Cape al-Hadd in Oman and the Gwadar Bay on the Iran-Pakistan border. It is approximately 560 km long. Some of the significant islands that are located in the Gulf of Oman include Sheytan Island, Al Fahal Island, Dimaniyat Islands, and the Sawadi Islands.
The Gulf of Oman historically and geographically has been referred to with different names by Arabian, Iranian, Indian, Pakistani and European geographers and travelers, including Makran Sea and Akhzar Sea.[8][9]
Makran Sea
Akhzar Sea
Persian Sea (Consist of whole of Persian gulf and gulf of Oman)
Until the 18th century it was known as Makran Sea and is also visible on historical maps and museums.
The countries bordering the Gulf of Oman include Iran, Oman, the United Arab Emirates, and Pakistan.
Muscat, the capital of Oman, is located on the coast of the gulf. The major Iranian cities that are located on the coastline of the Gulf of Oman are Gawadar Bay, Jask, and Chabahar.
The major international shipping ports that are situated in the Gulf of Oman include Port Sultan Qaboos Muttrah in Muscat, Oman; Chabahar Port in Iran; the Port of Fujairah and Khor Fakkan Container Terminal in the United Arab Emirates.
About 530 species of fish are found in the Gulf of Oman. Some of the notable fish include tuna, marlin, pomfret, swordfish, rainbow sardine, mackerel, sailfish, greater lizardfish, sardinella, and common dolphinfish. Some of the sharks that are found here are the Blue shark, silky shark, scalloped hammerhead, and bigeye thresher.
Scientists and researchers have confirmed that one of the world’s largest “dead zones” measuring approximately 165,000 km2 has been found in the Gulf of Oman. These hypoxic dead zones are incapable of supporting aquatic flora and fauna.
In 2018, scientists confirmed the Gulf of Oman contains one of the world’s largest marine dead zones, where the ocean contains little or no oxygen and marine wildlife cannot exist. The dead zone encompasses nearly the entire 165,000-square-kilometre (63,700 sq mi) Gulf of Oman, equivalent to the size of Florida, United States of America. The cause is a combination of increased ocean warming and increased runoff of nitrogen and phosphorus from fertilizers.
Anthropogenic agricultural activities have led to an increase in nitrogen-rich chemical fertilizers and pesticides along with phosphorus-based detergents that are eventually washed away by rains or by rivers into the aquatic ecosystems. These nutrients favor the growth of algae and result in algal blooms. When these algae die, they lead to deterioration in the water quality and depletion of dissolved oxygen in the water bodies. Over the years, these water bodies turn into “dead zones.”
The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of the Gulf of Oman as follows:
On the Northwest: A line joining Ràs Limah (25°57’N) on the coast of Arabia and Ràs al Kuh (25°48’N) on the coast of Iran (Persia).
On the Southeast: The Northern limit of the Arabian Sea [A line joining Ràs al Hadd, East point of Arabia (22°32’N) and Ràs Jiyùni (61°43’E) on the coast of Pakistan].
Why Persian Gulf is called Persian?
In 550 BC, the Achaemenid Empire established the first ancient empire in Persis (Pars, or modern Fars), in the southwestern region of the Iranian plateau. Consequently, in the Greek sources, the body of water that bordered this province came to be known as the “Persian Gulf”.
