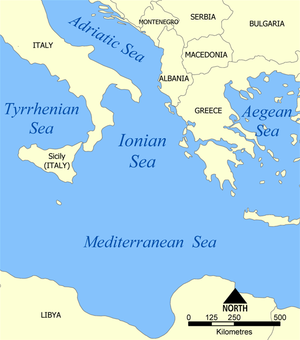
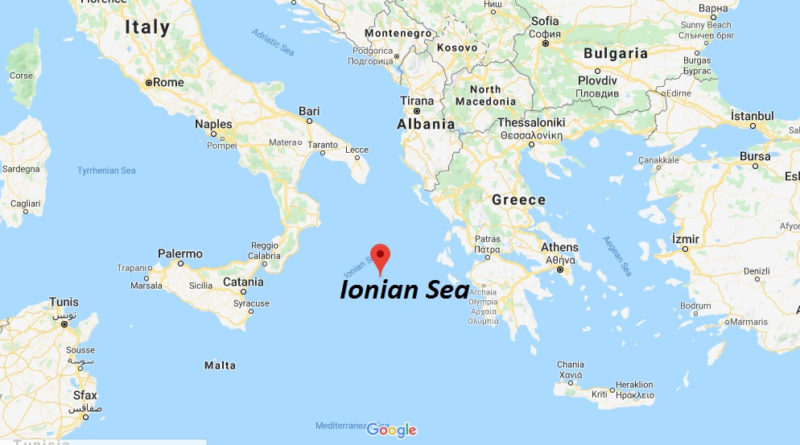
Ionian Sea, Latin Mare Ionium, Italian Mare Ionio, part of the Mediterranean Sea, lying between Albania (northeast), Greece (east), Sicily (southwest), and Italy (west and northwest).. The Sea was the location of the famous naval battle between Octavian and Marc Antony known as The Battle of Actium, a war fought in 31 BC, and is also famous for the hero from Ancient Greek mythology named Odysseus, who was from the island of Ithaca.
The Greek Blue colour refers to the sky as much as it does to the sea. This glorious blue colour is due partly to the reflection of the blue skies and partly to the fact that the sea does not contain large quantities of solid matter such as plankton, mud and dust floating in the water.
The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of the Ionian Sea as follows:
On the North. A line running from the mouth of the Butrinto River (39°44’N) in Albania, to Cape Karagol in Corfu (39°45’N), along the North Coast of Corfu to Cape Kephali (39°45’N) and from thence to Cape Santa Maria di Leuca in Italy.
On the East. From the mouth of the Butrinto River in Albania down the coast of the mainland to Cape Matapan.
On the South. A line from Cape Matapan to Cape Passero, the Southern point of Sicily.
On the West. The East coast of Sicily and the Southeast coast of Italy to Cape Santa Maria di Leuca.
The Ionian Sea (Greek: Ιόνιο Πέλαγος, Iónio Pélagos [iˈonio ˈpelaɣos]; Italian: Mar Ionio [mar ˈjɔːnjo]; Albanian: Deti Jon [dɛti jɔn]) is an elongated bay of the Mediterranean Sea. It is connected to the Adriatic Sea to the north, and is bounded by Southern Italy, including Calabria, Sicily, and the Salento peninsula to the west, southern Albania (and western Apulia, Italy) to the north, and the west coast of Greece, including the Peloponnese.
All major islands in the sea, which are located in the east of the sea, belong to Greece. They are collectively named the Ionian Islands, the main ones being Corfu, Kefalonia, Zakynthos, Lefkada, and Ithaca.
There are ferry routes between Patras and Igoumenitsa, Greece, and Brindisi and Ancona, Italy, that cross the east and north of the Ionian Sea, and from Piraeus westward. Calypso Deep, the deepest point in the Mediterranean at 5,109 m (16,762 ft), is in the Ionian Sea, at 36°34′N 21°8′E. The sea is one of the most seismically active areas in the world.
Can you swim in the Ionian Sea?
Enjoy the Ionian sun while swimming in the crystal-clear waters of the Ionian Sea.
Is Ionian Sea colder?
Here is a review of current sea surface temperatures around the country. Generally very warm Ionian sea and central Mediterranean, slightly ‘cooler’ Aegean sea. The western coast of Greece, including the islands Corfu, Lefkada and Cephalonia is very warm, with sea surface temperatures in 28-30 °C range.
Is the Ionian Sea safe?
The Ionian is generally a safe sea, one which is not affected by the high meltemi winds that are found in Eastern Greece.
Why is it called Ionian?
They were named Ionians after Ion the son of Xuthus.
Is Ionian Sea warm?
The warmest water in The Ionian Sea was recorded today in Kalamata. The water temperature in this location is 61°F. And the coldest in Porto Cesareo, its value 56°F.
Is there sharks in Ionian Sea?
Common thresher shark, blue shark, bluntnose sixgill shark and shortfin mako are the most observed species in Adriatic and Ionian seas, respectively.
Which is better Ionian or Aegean sea?
Generally, for those who seek peace, quiet and gentle sailing the Ionian is for you while for those who seek something a bit wilder you can find all you need on the Aegean, from the big winds to the huge evenings out!

Are there jellyfish in the Ionian Sea?
There have been numerous reports of purple jellyfish in the Cyclades, in the Ionian Sea, in the Peloponnese and some parts of Crete, but according to recent reports, the Ionian Sea currently has almost no problem with jellyfish, unlike the Aegean sea, where they appear sporadically.
Are there dolphins in the Ionian Sea?
The Inner Ionian Sea Archipelago (site code GR2220003), where we study common dolphins, bottlenose dolphins and Mediterranean monk seals. The Gulf of Ambracia (GR2110001), where bottlenose dolphins are the only cetacean species present.
Why is the Ionian Sea so salty?
The high water temperature (up to 83°F) causes a high rate of evaporation, and the sea’s salinity is also in part due to its remoteness from land: it receives no fresh-water inflow.
What language do Ionians speak?
Ionic dialect, any of several Ancient Greek dialects spoken in Euboea, in the Northern Cyclades, and from approximately 1000 bc in Asiatic Ionia, where Ionian colonists from Athens founded their cities. Attic and Ionic dialects together form a dialect group.
Places
From south to north in the west, then north to south in the east:
Syracuse, port, W
Catania, port, W
Messina, port, W
Taranto, port N
Himara, small port, NE
Saranda, port and a beach, NE
Kerkyra, port, E
Igoumenitsa, port, E
Parga, small port, E
Preveza, port, E
Astakos, port, E
Argostoli, port, E
Patra, port, E
Kyparissia, port, E
Pylos, port, E
Methoni, small port and a beach
Ionian Islands
Gulfs and straits
Strait of Messina, W
Gulf of Catania, W
Gulf of Augusta, W
Gulf of Taranto, NW
Gulf of Squillace, NW
Ambracian Gulf, E
Gulf of Patras, connecting the Gulf of Corinth, ESE
Gulf of Kyparissia, SE
Messenian Gulf, SE
Laconian Gulf, ESE
Islands
Corfu
Kefalonia
Ithaca
Zakynthos
Lefkada
Paxi
Kythira
Islets
Antikythera
Antipaxi
Arkoudi
Atokos
Kalamos
Kastos
Ksamil Islands
Kravia
Kythros
Lazareto (Ithaca)
Lazaretto (Corfu)
Meganisi
Navtilos
Pontikonisi
Proti
Sphacteria
Skorpios
Sparti (Lefkada)
Stillo
Strofades
Tongo
Vido
