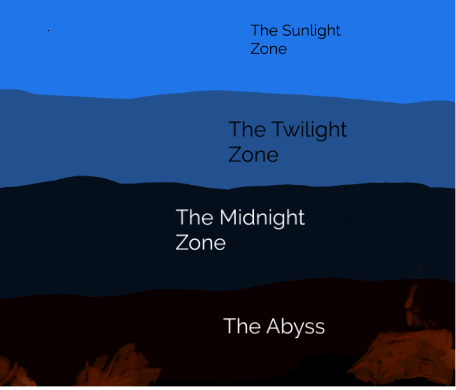
The Midnight Zone is the part of the ocean where more than 75 percent of all the ocean’s water lies. It starts at 3,281 feet below the surface and goes all the way to a depth of 13,124 feet (1,000–4,000 meters). That’s almost 3 miles!
Aphotic means “no light,” and this part of the ocean is called the aphotic zone because absolutely no natural light reaches this deep. It’s also referred to as the bathypelagic zone—bathy means “deep water.”
Midnight Zone: Ninety percent of the ocean is in the midnight zone. It is entirely dark—there is no light. The water pressure is extreme. The deepest was almost 11,000 meters (36,000 feet) down—deeper than Mount Everest is tall. To withstand such crushing pressures, the sub’s two-person crew compartment is wrapped in a nine-centimeter (3.5-inch) titanium cocoon. It also carries up to 96 hours’ worth of emergency oxygen. Midnight Zone: This zone extends from 1,000 meters (3,300 feet) to 4,000 meters (13,100 feet). No sunlight reaches this layer and the temperature is a constant 39°F (4°C).
Hadalpelagic Zone – Beyond the abyssopelagic zone lies the forbidding hadalpelagic zone. This layer extends from 6,000 meters (19,686 feet) to the bottom of the deepest parts of the ocean.