Principles of the Law of the Sea Versus Maritime Security, Combined Maritime Forces (CMF), foreign-flagged vessel, law of the sea, Maritime Security, maritime security awareness (MSA), Principles of the Law of the Sea, UNCLOS
View More Principles of the Law of the Sea Versus Maritime SecurityCategory: Law of the sea
The law of the sea is a body of customs, treaties, and international agreements by which governments maintain order, productivity, and peaceful relations on the sea. NOAA’s nautical charts provide the baseline that marks the inner limit of the territorial sea and the outer limit of internal waters.
how The SUA Protocol 2005 mechanism working in the law of the sea? (about Convention for the Suppression of Unlawful Acts Against the Safety of Maritime Navigation)
how The SUA Protocol 2005 mechanism working in the law of the sea? (about Convention for the Suppression of Unlawful Acts Against the Safety of Maritime Navigation), Convention for the Suppression of Unlawful Acts Against the Safety of Maritime Navigation, SUA Protocol 2005, UNSC, WMD
View More how The SUA Protocol 2005 mechanism working in the law of the sea? (about Convention for the Suppression of Unlawful Acts Against the Safety of Maritime Navigation)what is the meaning of Proliferation Security Initiative (PSI)?
what is the meaning of Proliferation Security Initiative (PSI)?, military efforts against terrorism, NATO, Proliferation Security Initiative (PSI), PSI, WMD
View More what is the meaning of Proliferation Security Initiative (PSI)?what is the meaning of Expanded MIO and Maritime Security Operations(MSO)?
Maritime embargo operations in support of economic sanctions have been called by some traditional or limited MIO. AS stated above, the reaction to 9/11 expanded the use of MIO to hostilities. This subsequently introduced MIO as an instrument against the wider terrorist threat beyond Al Qaida and its supporters and beyond Afghanistan.
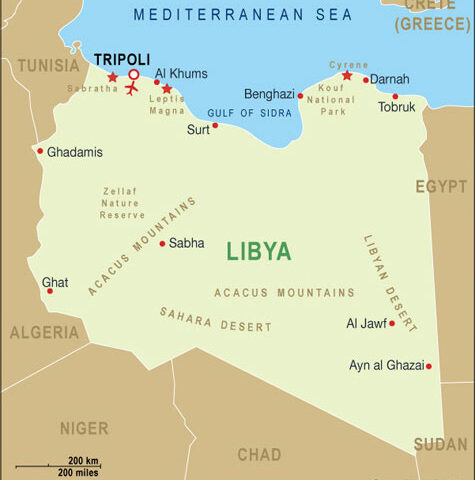
View More what is the meaning of Expanded MIO and Maritime Security Operations(MSO)?History of Maritime Interception Operations, Libya (2011–Present)
History of Maritime Interception Operations, Libya (2011–Present), Libya, Libyan leader Qaddafi, Libyan port of Es Sidra, Maritime Interception Operations, NATO, UNSC
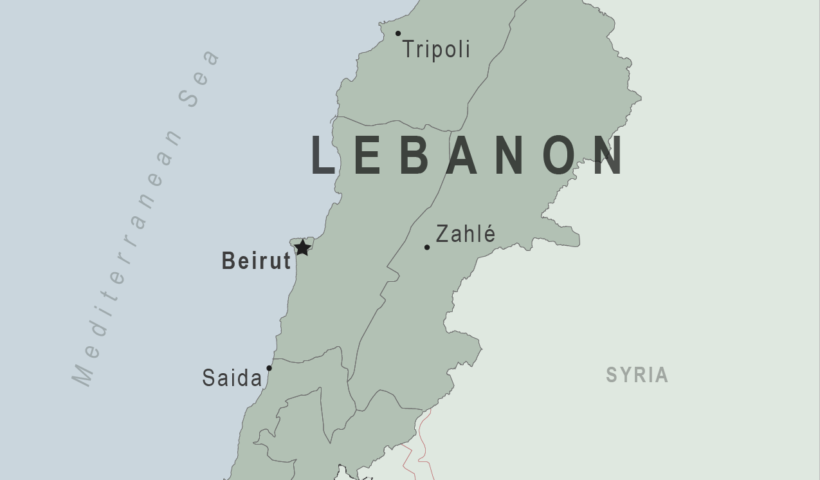
View More History of Maritime Interception Operations, Libya (2011–Present)History of Maritime Interception Operations, Lebanon (2006–Present)
History of Maritime Interception Operations, Lebanon (2006–Present), Israel and Hezbollah, lebanon, maritime dimension: Maritime Taskforce, Maritime Interception Operations, UNSC
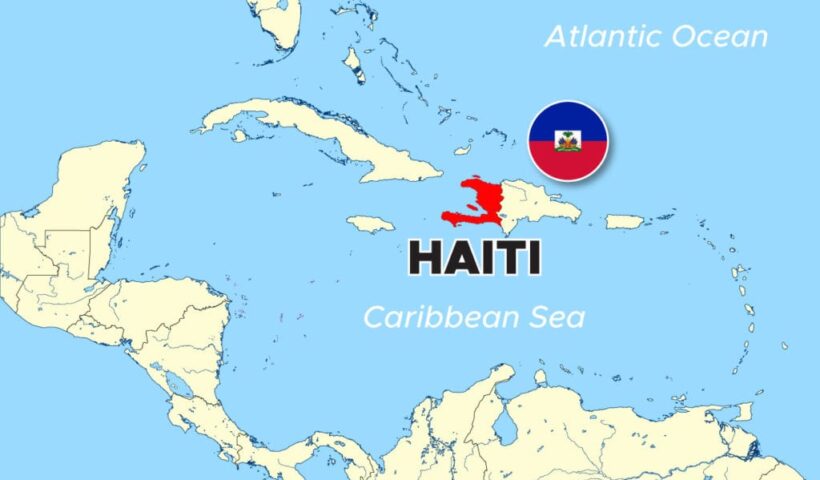
View More History of Maritime Interception Operations, Lebanon (2006–Present)History of Maritime Interception Operations, Haiti (1993–1996)
History of Maritime Interception Operations, Haiti (1993–1996), Haiti, Maritime Interception Operations, multinational force (MNF), OAS, Organization of American States, UNSC
View More History of Maritime Interception Operations, Haiti (1993–1996)History of Maritime Interception Operations, The Former Yugoslavia (1992–1996)
History of Maritime Interception Operations, The Former Yugoslavia (1992–1996), Adriatic Sea, Maritime Interception Operations, NATO, The Former Yugoslavia, UNSC, WEU
View More History of Maritime Interception Operations, The Former Yugoslavia (1992–1996)History of Maritime Interception Operations, Iraq (1990–2003)
History of Maritime Interception Operations, Iraq (1990–2003), Iraq, Maritime Interception Force (MIF), Maritime Interception Operations, UN Charter, UNSC
View More History of Maritime Interception Operations, Iraq (1990–2003)Can a Coastal State Conduct Marine Scientific Research in the Disputed Areas Without Consent from the Other Coastal State?
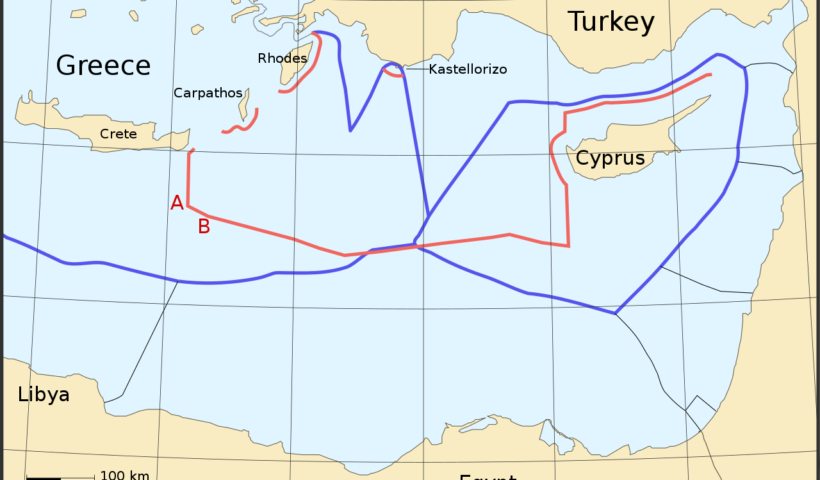
Can a Coastal State Conduct Marine Scientific Research in the Disputed Areas Without Consent from the Other Coastal State?, Aegean Sea Continental Shelf Case, Article 245 of the LOSC, Article 246 of the LOSC, Chinese exploration activities in the East China Sea, coastal State, East China Sea, exclusivity of knowledge, Greece, ICJ, ICSU, ILC, International Council of Scientific Union, International Law Commission, LOS Convention, Research in the Disputed Areas, sea-bed, sea-bed and subsoil of the continental shelf, seismic exploration, turkey
View More Can a Coastal State Conduct Marine Scientific Research in the Disputed Areas Without Consent from the Other Coastal State?Can a Third State Conduct Marine Scientific Research in a Disputed Area Without Consent from Any of Two Coastal States?
Can a Third State Conduct Marine Scientific Research in a Disputed Area Without Consent from Any of Two Coastal States?, coastal States, marine scientific research by a third State, Third State Conduct Marine Scientific Research in a Disputed Area
View More Can a Third State Conduct Marine Scientific Research in a Disputed Area Without Consent from Any of Two Coastal States?Legal Nature of Maritime Delimitation in law of the sea and customary international law
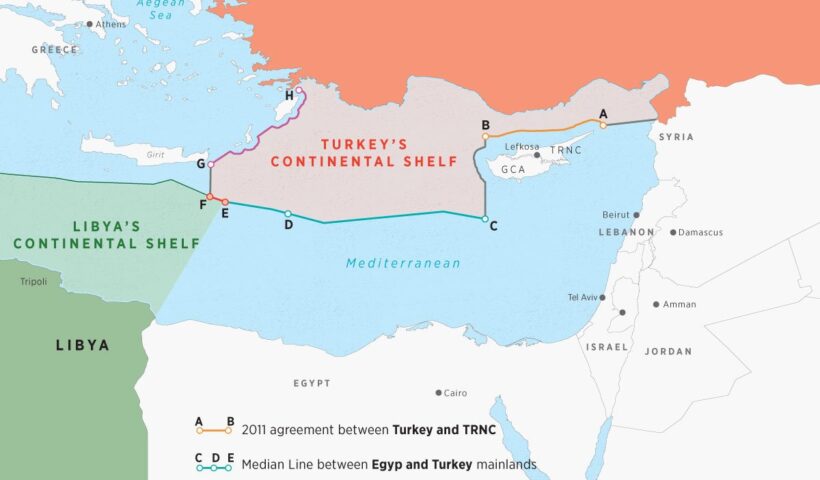
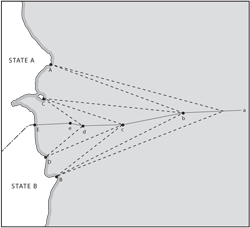
Maritime delimitation may be defined as the process of establishing lines separating the spatial ambit of coastal State jurisdiction over maritime space where the legal title overlaps with that of another State. This definition calls for five comments:… Legal Nature of Maritime Delimitation in law of the sea and customary international law, a just and equitable share, continental shelf, délimitation constitutive, délimitation déclarative, EEZ, geographical co-ordinates, Gulf of Maine case, internal waters, International Sea-Bed Authority, maritime delimitation, North Sea Continental Shelf cases, provisional delimitation line, territorial sea, What are the stages of maritime boundary?, What is a single maritime boundary?, What is delimited boundary?, What is maritime space?, What is median line principle?, What is the difference between demarcation and delimitation?, Which law delimits world seas?
View More Legal Nature of Maritime Delimitation in law of the sea and customary international lawlegal definition of an enclosed or semi-enclosed sea
An enclosed sea was not a fully closed sea such as the Caspian Sea or the Aral Sea, which had no outlets to the oceans. It was, instead, a small body of inland water, such as the Persian Gulf and the Baltic Sea, which had at least one outlet to the open sea.
On the other hand, he explained that the term ‘semi-enclosed sea’:
[…] could be used in a broad sense to cover larger sea basins along the margins of the main ocean basins, more or less enclosed by a land mass whether continental or insular – and with one or more narrow outlets to the oceans.. legal definition of an enclosed or semi-enclosed sea, Aral Sea, Article 122 at UNCLOS III, Baltic Sea, Caspian Sea, closed seas, Dead Sea, enclosed sea, Mediterranean sea, open sea, Persian Gulf, semi-enclosed sea, UNCLOS
Recent Developments about piracy in law of the sea and customary international law
In general the difficulties created by recent incidents of piracy and violentacts against shipping have not been due to doubts or disagreementabout the proper characterization…
View More Recent Developments about piracy in law of the sea and customary international lawPiracy in the Traditional Law of the Sea
Piracy in the Traditional Law of the Sea, 1988 SUA Convention, armed robbery, armed robbery against ships, Gulf Aden, IMO, Piracy, self-defence, Straits of Malacca, territorial sea, armed robbery against ships, Convention on the Suppression of Unlawful Acts Against the Safety of Maritime Navigation, IMO, International Maritime Organization, international shipping, Piracy
View More Piracy in the Traditional Law of the SeaDelimitation of the Continental Shelf Beyond 200 Nautical Miles in law of the sea and customary international law
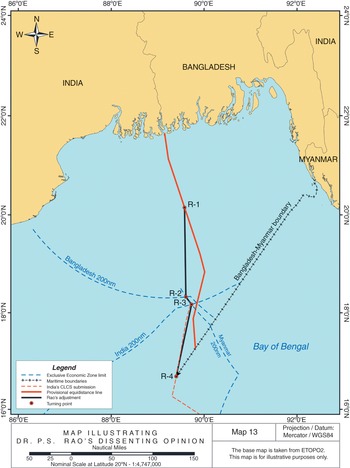
The delimitation of the continental shelf beyond 200 nautical miles is a comparatively new subject in the law of maritime delimitation. In this regard, three issues need further consideration: (i) entitlements to the continental shelf beyond 200 nautical miles, (ii) the relationship between the CLCS and an international court or tribunal, and (iii) the methodology.. Delimitation of the Continental Shelf Beyond 200 Nautical Miles in law of the sea and customary international law, Bangladesh/India case, Bangladesh/Myanmar case, continental shelf, Delimitation of the Continental Shelf, Delimitation of the Continental Shelf Beyond 200 Nautical Miles, Ghana/Côte d’Ivoire cases, LOSC, maritime delimitation, What are the characteristics of the continental shelf?, What does continental slope mean?, What extended continental shelf?, What is continental shelf limit?, What is the importance of continental shelf?, What is the largest continental shelf?, Where is the continental shelf?
View More Delimitation of the Continental Shelf Beyond 200 Nautical Miles in law of the sea and customary international lawJudicial Creativity in the Law of Maritime Delimitation
Judicial Creativity in the Law of Maritime Delimitation, Anglo-French Continental Shelf Arbitration, Gulf of Maine cases, maritime delimitation, opinio juris, What are the stages of maritime boundary?, What is a single maritime boundary?, What is delimited boundary?, What is maritime space?, What is median line principle?, What is the difference between demarcation and delimitation?, Which law delimits world seas?
View More Judicial Creativity in the Law of Maritime DelimitationEnvironmental Factors as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international law
While protection of the marine environment is a matter of important concern, the existing case law seems to pay little attention to environmental concern in the context of maritime delimitations. In the Gulf of Maine case, the United States relied on environmental factors to justify an equitable maritime boundary. However, the Chamber of the ICJ discarded the ecological criterion primarily because such a criterion was inconsistent with the ‘neutral criteria’ for drawing a single maritime boundary. Usually environmental considerations have played little, if any, role in agreements concerning maritime delimitations.. Environmental Factors as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international law, delimitation process, Environmental Factors, equitable maritime boundary, Gulf of Maine case, marine environment, maritime boundary, relevant circumstances
View More Environmental Factors as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international lawNavigational Factors as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international law
Navigational Factors as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international law, delimitation process, Eritrea/Yemen Arbitration, Guyana/Suriname case, LOSC, Navigational Factors, navigational interests, relevant circumstances, territorial seas
View More Navigational Factors as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international lawSecurity Interests as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international law
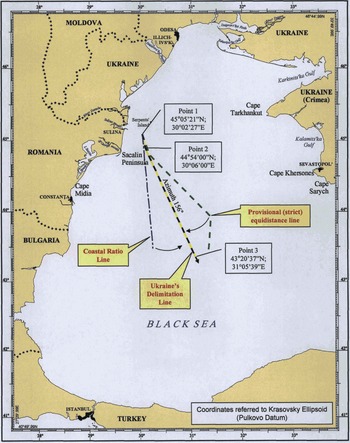
Security Interests as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international law, Black Sea cases, delimitation process, Greenland/Jan Mayen case, Libya/Malta case, relevant circumstances, security factors, Security Interests
View More Security Interests as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international lawHistoric Title and Historic Rights as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international law
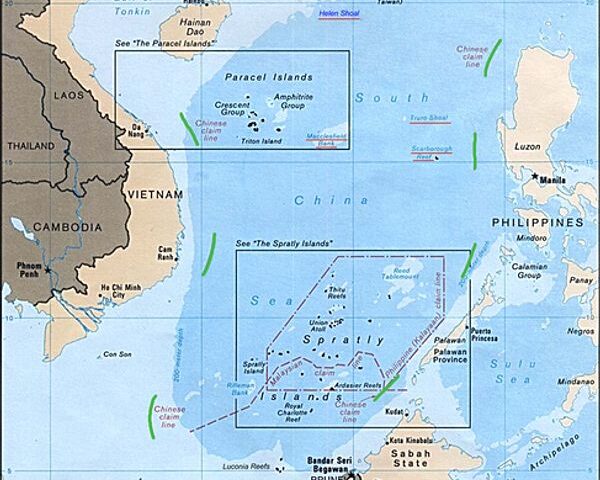
Historic Title and Historic Rights as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international law, continental shelf delimitation, delimitation process, EEZ, EEZ delimitation, historic rights, Historic Title, LOSC, maritime areas, maritime delimitation, relevant circumstances, South China Sea Arbitration
View More Historic Title and Historic Rights as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international lawConduct of the Parties as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international law
Conduct of the Parties as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international law, Conduct of the Parties, delimitation process, maritime delimitation, Tunisia/ Libya judgment
View More Conduct of the Parties as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international lawEconomic Factors as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international law
Economic Factors as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international law, Cameroon/Nigeria case, common deposit clause, continental shelf, Economic Factors, Eritrea/Yemen Arbitration, Greenland/Jan Mayen case, Gulf of Maine judgment, maritime delimitation, mineral deposit clause, natural resources
View More Economic Factors as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international lawPresence of Third States as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international law
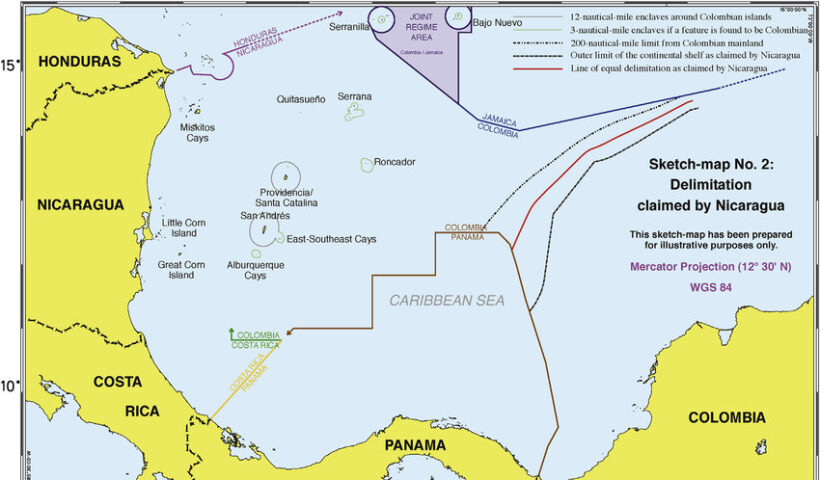
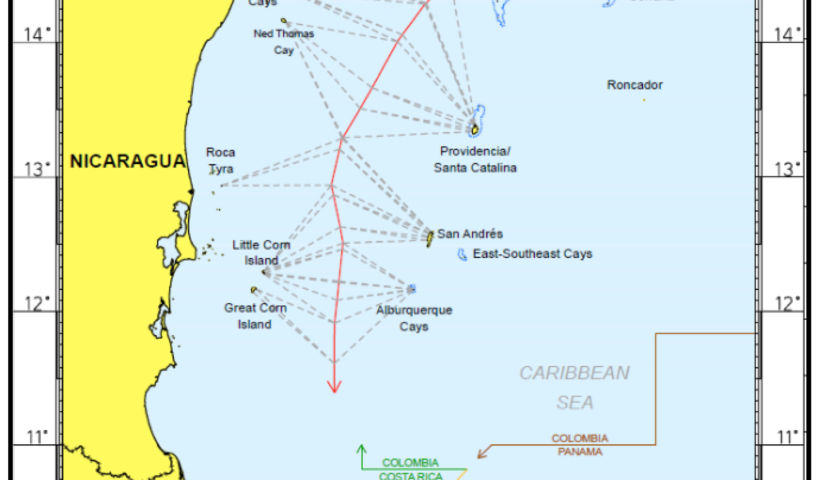
Presence of Third States as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international law, Nicaragua/Colombia case, Presence of Third States, principal relevant circumstances in the law of maritime delimitation
View More Presence of Third States as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international lawGeological and Geomorphological Factors as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international law
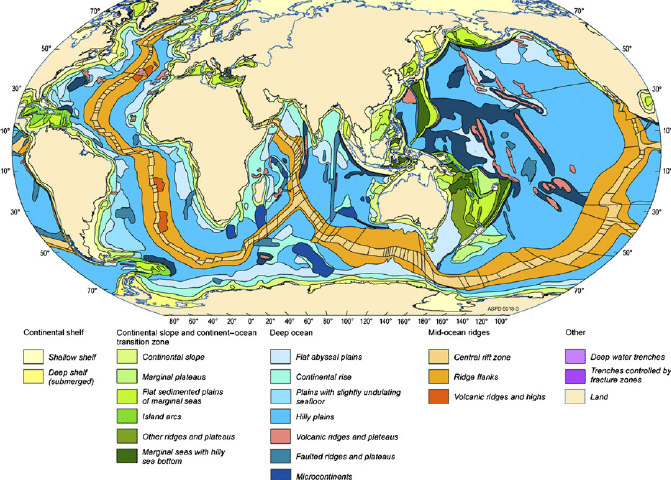
Geological and Geomorphological Factors as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international law, continental shelf, delimitation process, Geological, Geomorphological, relevant circumstances
View More Geological and Geomorphological Factors as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international lawPresence of Islands as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international law
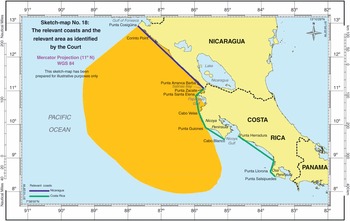
Presence of Islands as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international law, 12-nautical-mile, Black Sea case, continental shelf, delimitation process, geographic realities, ICJ jurisprudence, ITLOS, maritime boundary, maritime delimitation, Nicaragua/ Colombia case, Nicaragua/Honduras case, Presence of Islands, Qatar/Bahrain case, relevant circumstances
View More Presence of Islands as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international lawBaselines or basepoints as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international law
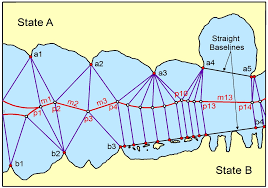
Baselines or basepoints as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international law, Baltic, baselines, basepoint, basepoints, delimitation process, equidistance method, Eritrea/Yemen case, Libya/Malta case, LOSC, Maritime Boundary Agreement between the United States and Cuba, maritime delimitations, relevant circumstances, straight-baselines system
View More Baselines or basepoints as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international lawProportionality as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international law
Proportionality as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international law, adjacent coasts, Anglo-French Continental Shelf case, delimitation process, Equitable Principles, existence of particular coastal configurations, ITLOS, maritime delimitation, North Sea Continental Shelf cases, Proportionality, quasi-equal length of the relevant coasts, relevant circumstances
View More Proportionality as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international lawConfiguration of Coasts as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international law
Configuration of Coasts as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international law, Bangladesh/India Arbitration, Bangladesh/Myanmar case, Configuration of Coasts, delimitation process, equidistance line, equidistance method, geographical factors, Guinea/ Guinea-Bissau case, ITLOS, Libya/Malta judgment, line grosso modo, macrogeography, manifestly concave, maritime delimitation, North Sea Continental Shelf cases, opposite and adjacent coasts, provisional equidistance line, relevant circumstances
View More Configuration of Coasts as a RELEVANT CIRCUMSTANCES in delimitation process in law of the sea and customary international lawDEVELOPMENT OF CASE LAW RELATING TO MARITIME DELIMITATION
DEVELOPMENT OF CASE LAW RELATING TO MARITIME DELIMITATION, 1977 Anglo-French Continental Shelf case, an equitable result, Bangladesh/India Arbitration, Bangladesh/Myanmar case, Black Sea case, Cameroon/Nigeria case, continental shelf, corrective-equity approach, EEZ, equidistance method, equidistance/relevant circumstances method, equitable criteria, Equitable Principles, equitable result, Eritrea/Yemen Arbitration, Ghana/Côte d’Ivoire case, Greenland/Jan Mayen case, Gulf of Maine case, Guyana/Suriname Arbitration, maritime delimitation, Nicaragua/Honduras case, North Sea Continental Shelf judgment, Pierre and Miquelon Arbitration, provisional delimitation line, Qatar/Bahrain case, relevant circumstances, resultorientated equity approach, single combined equidistance–special circumstances rule, special circumstances, test of disproportionality, three-stage approach to maritime delimitations, Tunisia/Libya case, What are the stages of maritime boundary?, What is a single maritime boundary?, What is delimited boundary?, What is maritime space?, What is median line principle?, What is the difference between demarcation and delimitation?, Which law delimits world seas?
View More DEVELOPMENT OF CASE LAW RELATING TO MARITIME DELIMITATIONTREATY LAW CONCERNING MARITIME DELIMITATION
TREATY LAW CONCERNING MARITIME DELIMITATION, 1958 Convention on the Continental Shelf, 1977 Anglo-French Continental Shelf case, continental shelf, Delimitation of the contiguous zone, delimitation of the territorial seas, determining the applicable law, EEZ, equidistance (median line), Equitable Principles, equitable solution, inequitable results, LOSC, method of delimitation, special circumstances, TSC, What are the stages of maritime boundary?, What is a single maritime boundary?, What is delimited boundary?, What is maritime space?, What is median line principle?, What is the difference between demarcation and delimitation?, Which law delimits world seas?
View More TREATY LAW CONCERNING MARITIME DELIMITATIONCONCEPT OF MARITIME DELIMITATION in law of the sea and customary international law
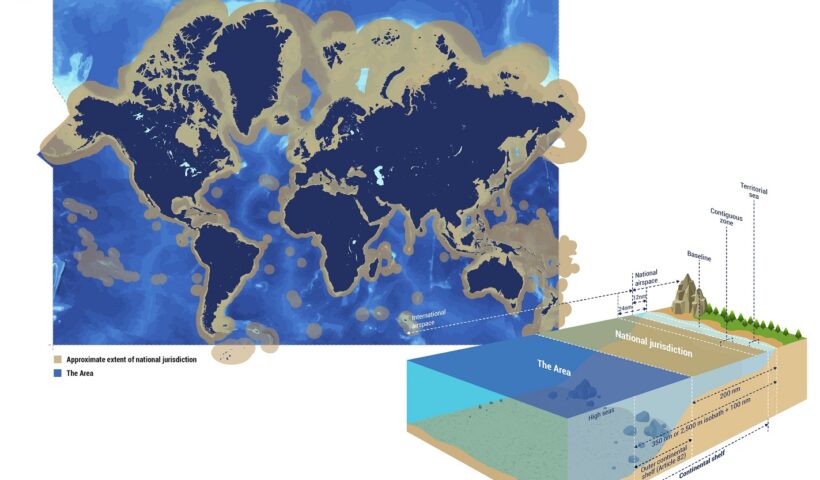
CONCEPT OF MARITIME DELIMITATION in law of the sea and customary international law, coastal State jurisdiction over maritime space, delimitation of internal waters, Delimitation of the contiguous zone, Delimitation of the Continental Shelf, Delimitation of the EEZ, Delimitation of the territorial sea, Gulf of Maine case, maritime delimitation, maritime limits, maritime spaces, process of establishing lines, What are the stages of maritime boundary?, What is a single maritime boundary?, What is delimited boundary?, What is maritime space?, What is median line principle?, Which law delimits world seas?
View More CONCEPT OF MARITIME DELIMITATION in law of the sea and customary international lawwhat is the Main Issues of Maritime Delimitation in law of the sea and customary international law?
what is the Main Issues of Maritime Delimitation in law of the sea and customary international law?, advantages and disadvantages of the basic approaches to the law of maritime delimitations, approaches adopted by international courts and tribunals with regard to maritime delimitations, Main Issues of Maritime Delimitation, marine spaces, maritime delimitation, multiple jurisdictional zones, principal relevant circumstances in the law of maritime delimitation, principle applicable to maritime delimitations, role of international courts and tribunals in the development of the law of maritime delimitations, What are the stages of maritime boundary?, What is a single maritime boundary?, What is delimited boundary?, What is maritime space?, What is median line principle?, Which law delimits world seas?
View More what is the Main Issues of Maritime Delimitation in law of the sea and customary international law?The 1994 Implementation Agreement about seabed area, under view of law of the sea
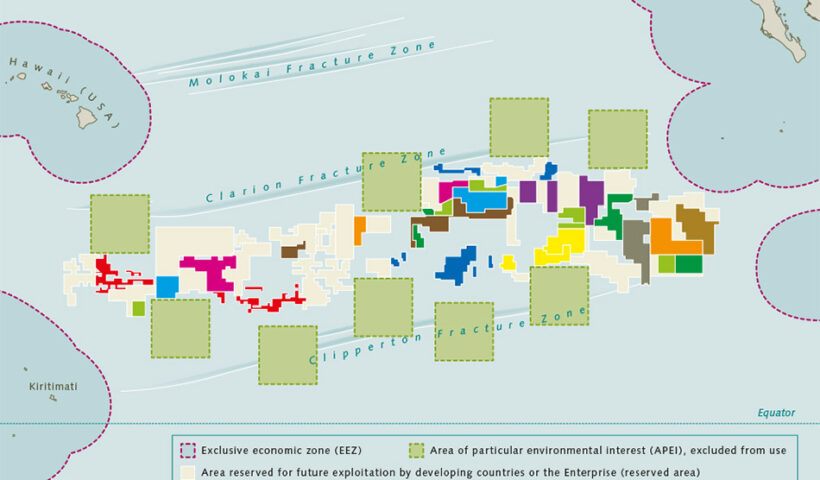
The 1994 Implementation Agreement about seabed area, under view of law of the sea, ‘mini-treaty’ regime, 1994 Implementation Agreement, Common Heritage of Mankind, Cost-effectiveness, Economic assistance: In order to assist developing countries, Financial terms of contracts, International Seabed Authority Endowment Fund for Marine Scientific Research in the Area, LOSC, Market-orientated Approaches, Production policies, seabed Area, The obligation to transfer technology, UNCLOS III
View More The 1994 Implementation Agreement about seabed area, under view of law of the seaObligations and Liability of Sponsoring States about seabed area in law of the sea and customary international law
Obligations and Liability of Sponsoring States about seabed area in law of the sea and customary international law, area, ITLOS, LOSC, obligation to apply a precautionary approach, obligation to apply best environmental practices, obligation to assist the Authority in the exercise of control over activities in the Area, obligation to cooperate with the Authority in the establishment and implementation of programmes for monitoring and evaluating the impacts of deep seabed mining on the marine environment, obligation to ensure the availability of recourse for compensation in respect of damage caused by pollution, obligation to take measures to ensure the provision of guarantees in the event of an emergency order by the Authority for protection of the marine environment, responsibility to ensure, seabed Area
View More Obligations and Liability of Sponsoring States about seabed area in law of the sea and customary international lawSystem for the Exploration and Exploitation of Resources of the seabed Area(common heritage materials)
Activities in the Area are to be carried out by the Enterprise and other commercial operators in accordance with Article 153(2) of the LOSC. The commercial operators include States Parties, State enterprises, natural or juridical persons which possess the nationality of States Parties or are effectively controlled by them or their nationals provided for in Article 153(2). This arrangement is called the ‘parallel system’. This system represents a compromise between various interest groups. Actually the LOSC provides three operational modes for deep seabed mining.
. System for the Exploration and Exploitation of Resources of the seabed Area(common heritage materials), Common Heritage, Exploration and Exploitation of Resources, LOSC, seabed Area
International Seabed Authority, its Jurisdiction, authorities and obligations in law of the sea and LOSC
The International Seabed Authority is an international organisation governing the Area and activities there. All States Parties to the LOSC are ipso facto members of the Authority. The Authority sits in Jamaica and comprises three principal organs, that is to say, an Assembly, a Council and a Secretariat. In addition, it has its operational organ, i.e. the Enterprise.
The Assembly, which consists of all the members of the Authority, is the supreme organ of the Authority to which the other principal organs shall be accountable as specifically provided for in the LOSC. The Assembly is entitled to establish general policies on any question or matter within the competence of the Authority.
The Council, which consists of thirty-six members of the Authority, is the executive organ of the Authority. Each member of the Council shall be elected for four years. The Council is empowered to establish the specific policies to be pursued by the Authority on any question or matter within the competence of the Authority.
The Secretariat of the Authority comprises a Secretary-General and such staff as the Authority may require. In the performance of their duties, the Secretary-General and the staff shall not seek or receive instructions from any government or from any other source external to the Authority. They shall refrain from any action which might reflect on their position as international officials responsible only to the Authority. In addition, the Secretary-General and the staff shall have no financial interest in any activity relating to exploration and exploitation in the Area. Those qualifications will contribute to secure the independence and neutrality of the Secretariat. International Seabed Authority, its Jurisdiction, authorities and obligations in law of the sea and LOSC, Cobalt-Rich Crusts Regulations, International Seabed Authority, ITLOS, Jamaica, LOSC, Polymetallic Nodules Regulations, seabed disputes chamber, the Sulphides Regulations
depth area on the high seas(sea-bed and ocean floor), legal aspects in law of the sea and customary international law
The exploration and exploitation of natural resources in the deep seabed is a new subject in the law of the sea. At the end of the nineteenth century, polymetallic nodules were discovered in the Arctic Ocean off Siberia. During the 1872 1877 scientific expedition of HMS Challenger, they were found to occur in most oceans of the world. Polymetallic nodules, which were also called manganese nodules, are small brown-black balls, usually between 1 and 20 centimetres in diameter. In the 1950s, attention was drawn to the economic significance of the nodules. During the International Geophysical Year of 1957–1958, polymetallic nodules were collected on the Tuamotu plateau approximately 370 kilometres east of Tahiti at a depth of some 900 metres. These nodules proved to contain commercially valuable minerals, such as nickel, copper and cobalt. Thus the exploration and exploitation of polymetallic nodules have attracted growing attention. As noted, the management of the deep seabed resources gave an impetus to convene UNCLOS III. The LOSC devotes Part XI to the regime governing the Area. depth area on the high seas(sea-bed and ocean floor), legal aspects in law of the sea and customary international law, Arvid Pardo, Common Heritage of Mankind, continental shelf, depth area on the high seas, natural resources, New International Economic Order, sea-bed and ocean floor, subsoil
View More depth area on the high seas(sea-bed and ocean floor), legal aspects in law of the sea and customary international lawRegulation of Migrant Smuggling by Sea in law of the sea and customary international law
Regulation of Migrant Smuggling by Sea in law of the sea and customary international law, 1979 International Convention on Maritime Search and Rescue, 2000 Migrant Smuggling Protocol, ECHR, European Convention on Human Rights, High seas, international human rights law, international refugee law, Lawfulness of Push-back Operations Against Migrants, Migrant Smuggling, SAR Convention, SOLAS Convention, Transnational Organised Crime, UN Convention against Transnational Organised Crime, UN High Commissioner for Refugees
View More Regulation of Migrant Smuggling by Sea in law of the sea and customary international lawExceptional Measures for Interception of Foreign Vessels on the High Seas based on law of the sea and customary international law
Exceptional Measures for Interception of Foreign Vessels on the High Seas based on law of the sea and customary international law, 1995 Council of Europe Agreement on Illicit Traffic by Sea, 2003 Agreement Concerning Co-operation in Suppressing Illicit Maritime and Air Trafficking in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances in the Caribbean Area, 2008 CARICIM Maritime and Airspace Security Co-operation Agreement, Convention on Psychotropic Substances, illicit traffic in narcotic drugs, Interception of Foreign Vessels, LOSC, Self-defence on the High Seas, Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, UN Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances
View More Exceptional Measures for Interception of Foreign Vessels on the High Seas based on law of the sea and customary international law