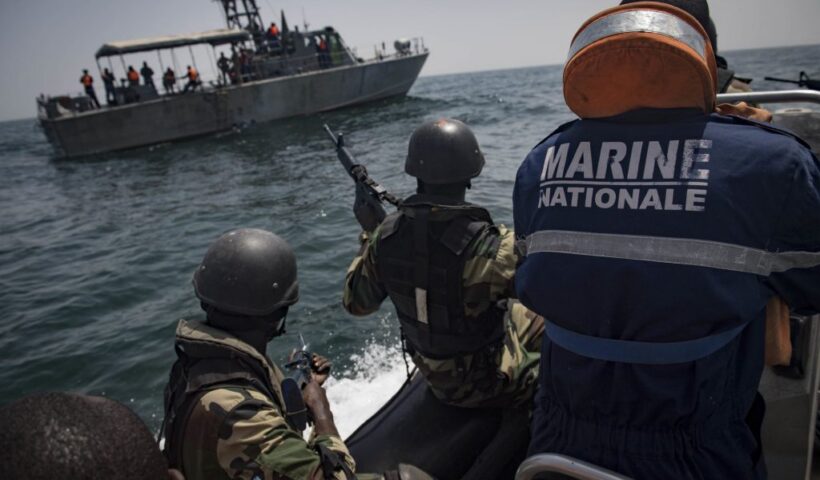
Exceptions to the Exclusive Jurisdiction of the Flag State on the law of the sea and customary international law, 1995 Council of Europe Agreement on Illicit Traffic by Sea, 2003 Agreement Concerning Co-operation in Suppressing Illicit Maritime and Air Trafficking in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances in the Caribbean Area, 2008 CARICIM Maritime and Airspace Security Co-operation Agreement, Convention on Psychotropic Substances, illicit traffic in narcotic drugs, Interception of Foreign Vessels, LOSC, Self-defence on the High Seas, Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, UN Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances
View More Exceptions to the Exclusive Jurisdiction of the Flag State on the law of the sea and customary international lawCategory: Law of the sea
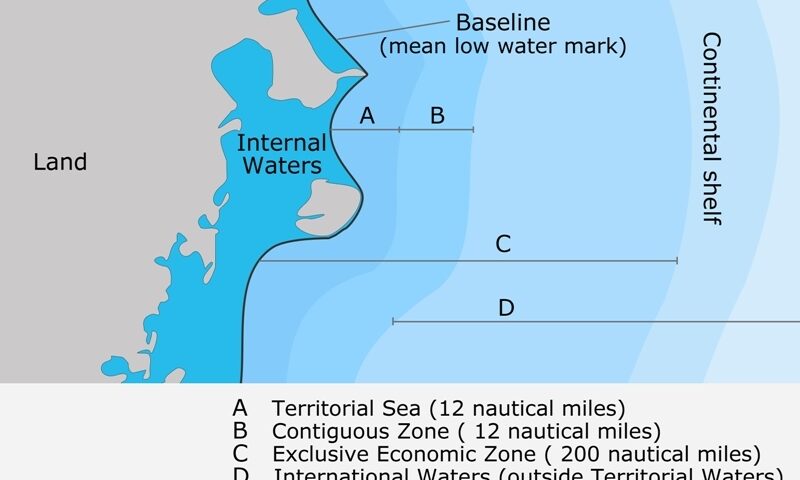
The law of the sea is a body of customs, treaties, and international agreements by which governments maintain order, productivity, and peaceful relations on the sea. NOAA’s nautical charts provide the baseline that marks the inner limit of the territorial sea and the outer limit of internal waters.
what is the meaning of Freedom of Navigation in law of the sea and customary international law
what is the meaning of Freedom of Navigation in law of the sea and customary international law, Arctic Sunrise Arbitration, LOSC, ship is without nationality, Ships With Suspicious Nationality, slave trade, unauthorized broadcasting, warship
View More what is the meaning of Freedom of Navigation in law of the sea and customary international lawwhat is the meaning of Flags of Convenience or open registry in the law of the sea and customary international law?
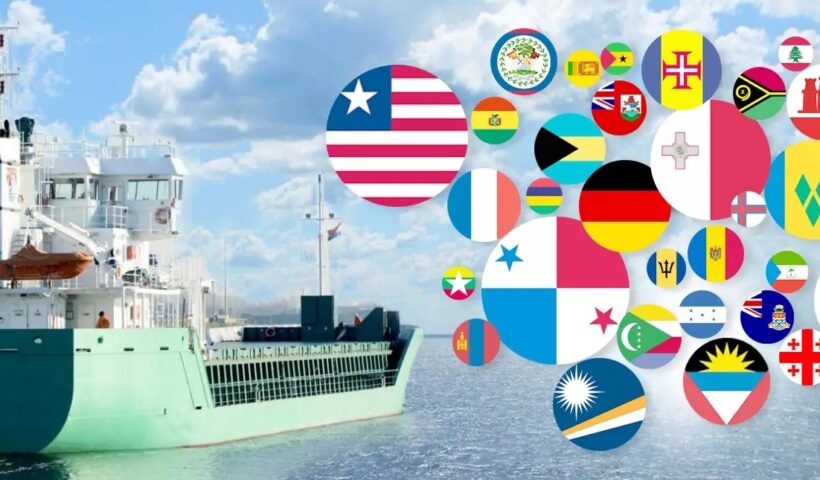
While there is no generally agreed definition, ‘flag of convenience’ or ‘open registry’ States refer, in essence, to States that permit foreign shipowners, having very little or virtually no real connection with those States, to register their ships under the flags of those States.
The flag of convenience States allow shipowners to evade national taxation and to avoid the qualifications required of the crews of their ships. In so doing, flag of convenience States give shipowners an opportunity to reduce crew costs by employing inexpensive labour, while these States receive a registry fee and an annual fee. As one of the few variables in shipping costs is crew costs, a highly competitive market within the international shipping industry prompts shipowners to resort to open registry States. what is the meaning of Flags of Convenience or open registry in the law of the sea and customary international law?, archipelagic sea, archipelagic waters, Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and their Disposal, COLREG, Convention on the International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea, De iure praedae, De mare clausum, De mare liberum, freedom of navigation, IMO, International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships, International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea, International Maritime Organization, international straits, maritime traffic, MARPOL, right of innocent passage, SOLAS, territorial sea, terrorism, United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea
the meaning of The Nationality of a Ship and flag states on the law of the sea and customary international law
The flag State jurisdiction is exercised on the basis of the nationality of a ship. Thus, the nationality of a ship is of central importance in order to establish the juridical link between a State and a ship flying its flag. Under international law, each State is entitled to determine conditions for the grant of its nationality to ships. In the M/V ‘Saiga’ case, ITLOS ruled:
Determination of the criteria and establishment of the procedures for granting and withdrawing nationality to ships are matters within the exclusive jurisdiction of the flag State. the meaning of The Nationality of a Ship and flag states on the law of the sea and customary international law, flag State jurisdiction, flag states, Grand Prince case, ITLOS, LOSC, Nationality of a Ship, Tomimaru case, UN Convention on Conditions for Registration of Ships
Principle of the Exclusive Jurisdiction of the Flag State in the law of the sea and customary international law
Principle of the Exclusive Jurisdiction of the Flag State in the law of the sea and customary international law, 1952 Brussels Convention for the Unification of Certain Rules relating to Penal Jurisdiction in Matters of Collision and Other Incidents of Navigation, 1966 International Convention on Load Lines, 1971 Agreement on Special Trade Passenger Ships, 1972 Convention on the International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea, 1974 International Convention for the SOLAS, 1976 ILO Convention No. 147 concerning Minimum Standards in Merchant Ships, 1993 Torremolinos Protocol, 1995 International Convention on Standards of Training, 2006 Maritime Labour Convention, Article 97 of the LOSC, Certification and Watchkeeping for Fishing Vessel Personnel (STCW-F), Certification and Watchkeeping for Seafarers, Exclusive Jurisdiction of the Flag State, ILO, IMO, International Convention for the Safety of Fishing Vessels, International Convention on Standards of Training, sail under its flag
View More Principle of the Exclusive Jurisdiction of the Flag State in the law of the sea and customary international lawPrinciple of the Freedom of the High Seas meaning in law of the sea and customary international law
Principle of the Freedom of the High Seas meaning in law of the sea and customary international law, Article 89 of the LOSC, Freedom of fishing, freedom of navigation, Freedom of overflight, Freedom of scientific research, Freedom of the High Seas, Freedom to construct artificial islands, Freedom to lay submarine cables and pipelines, LOSC, M/V ‘Louisa’ case, military activities
View More Principle of the Freedom of the High Seas meaning in law of the sea and customary international lawSpatial Scope of the High Seas in law of the sea and customary international law
The LOSC devotes Part VII to the high seas. Under Article 86, the high seas are defined as:
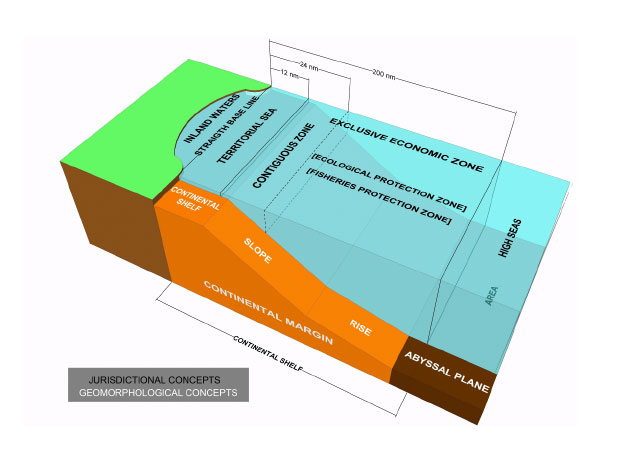
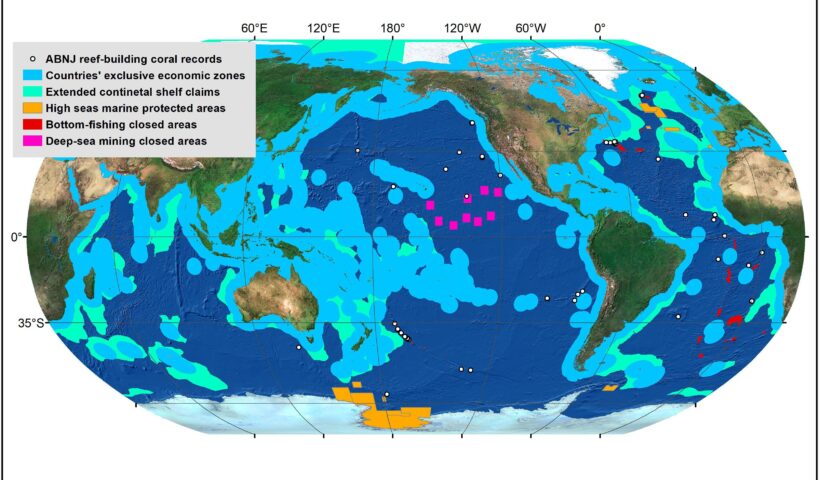
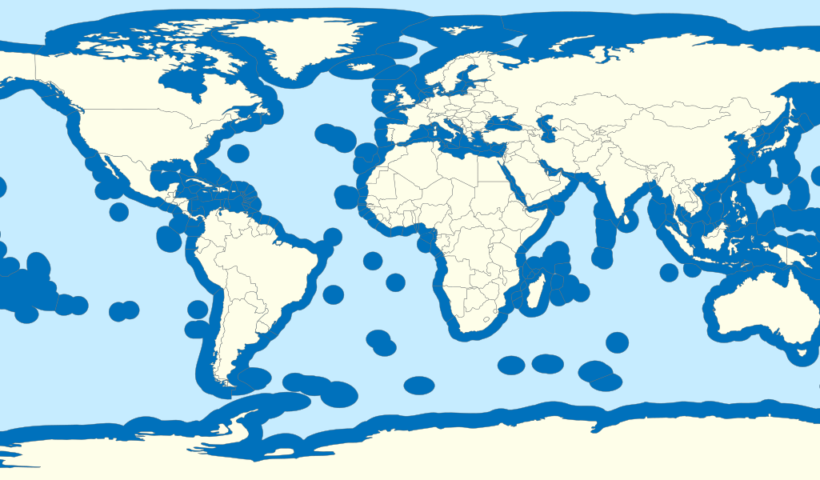
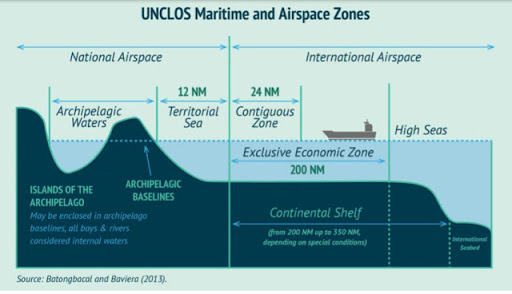
all parts of the sea which are not included in the EEZ, in the territorial sea or in the internal waters of a State, or in the archipelagic waters of an archipelagic State. Where a coastal State has established its EEZ, the landward limit of the high seas is the seaward limit of the EEZ. Where the coastal State has not claimed its EEZ, the landward limit of the high seas is the seaward limit of the territorial sea. In this case, the seabed of the high seas is the continental shelf of the coastal State up to the limit fixed by the international law of the sea. The seabed and subsoil beyond the outer limits of the continental shelf are the Area, which is the common heritage of mankind. The superjacent waters above the Area are always the high seas. Where the continental shelf extends beyond the limit of 200 nautical miles, the superjacent waters and the airspace above those waters are the high seas under Article 78 of the LOSC.. Spatial Scope of the High Seas in law of the sea and customary international law, EEZ, High seas, law of the sea, LOSC, seabed, Superjacent Waters
Protection of Archaeological and Historical Objects Found Within the Continental Shelf in the law of the sea and customary international law
It has been said that ‘the greatest museum of human civilization lies on the seabed’. Owing to the development of underwater archaeology as a scientific discipline, the protection of underwater cultural heritage has begun to emerge as a crucial issue in international law. Thus this section addresses two key instruments on this subject: the LOSC and the Convention on the Protection of Underwater Cultural Heritage adopted by UNESCO on 2 November 2001 (hereinafter the UNESCO Convention). . Protection of Archaeological and Historical Objects Found Within the Continental Shelf in the law of the sea and customary international law, Archaeological objects, continental shelf, Convention on the Protection of Underwater Cultural Heritage, EEZ, enclosed sea, Historical Objects, LOSC, semi-enclosed sea, underwater cultural heritage
View More Protection of Archaeological and Historical Objects Found Within the Continental Shelf in the law of the sea and customary international lawFreedoms of Third States on the continental shelf of other states based on the law of the sea and customary international law
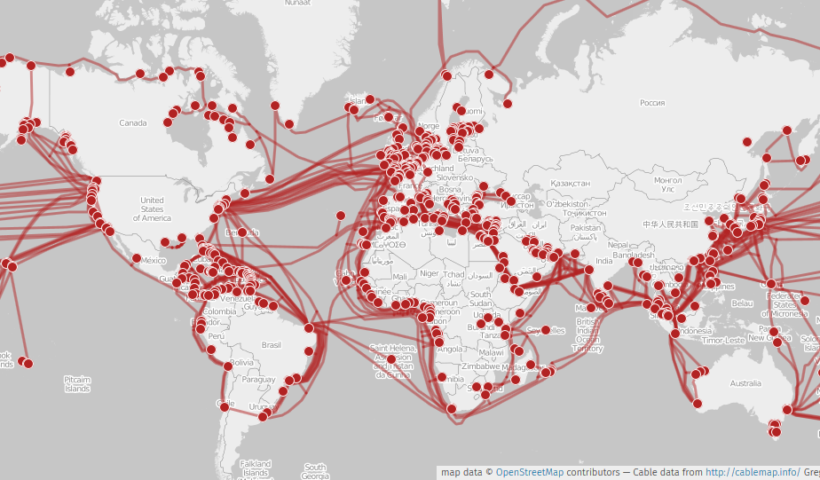
(a) Submarine Cables and Pipelines With respect to the freedom of use on the continental shelf, Article 79(1) stipulates that all States are entitled to lay submarine cables and pipelines on the continental shelf.
In practice, submarine cables are divided into two main categories: submarine power cables used to transmit electricity, and submarine communication cables used to transmit data communications traffic. At present, the overwhelming majority of the world’s international telecommunication relies on submarine fibre-optic cables, and submarine telecommunication cables have become a critical global communications infrastructure. The oil and gas pipeline is also of crucial importance as a reliable means of energy transport.
Freedoms of Third States on the continental shelf of other states based on the law of the sea and customary international law, continental shelf, EEZ, High seas, LOSC, marine pollution, Pipelines, Submarine Cables, Superjacent Waters
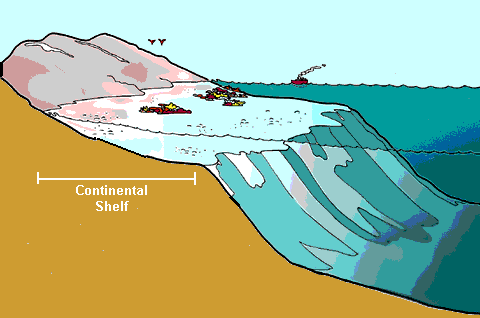
The Sovereign Rights of the Coastal State Over the Continental Shelf in law of the sea and customary international law
The coastal State exercises sovereign rights over the continental shelf for the purpose of exploring and exploiting its natural resources in accordance with Article 77(1). The principal features of sovereign rights can be summarised in six points:…The Sovereign Rights of the Coastal State Over the Continental Shelf in law of the sea and customary international law, coastal State, continental shelf, EEZ, inherent rights, LOSC, natural resources, non-living resources, Non-natural resources, Sovereign Rights
View More The Sovereign Rights of the Coastal State Over the Continental Shelf in law of the sea and customary international lawProcedures to Establish the Outer Limits of the Continental Shelf on the law of the sea and LOSC
Procedures to Establish the Outer Limits of the Continental Shelf on the law of the sea and LOSC, Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf, continental shelf, continental shelf in international law, continental shelf meaning, continental shelf unclos, geodetic data, LOSC, Outer Limits of the Continental Shelf, the continental shelf and its outer delimitation, The Establishment of the Outer Limits of the Continental Shelf, What are the limits of continental shelf?, What does the continental shelf of a coastal state comprise?, What is continental shelf in international law?, What is continental shelf theory?, What is the outer edge or ending point of the continental shelf?
View More Procedures to Establish the Outer Limits of the Continental Shelf on the law of the sea and LOSCThe Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf, duties, authorities and works
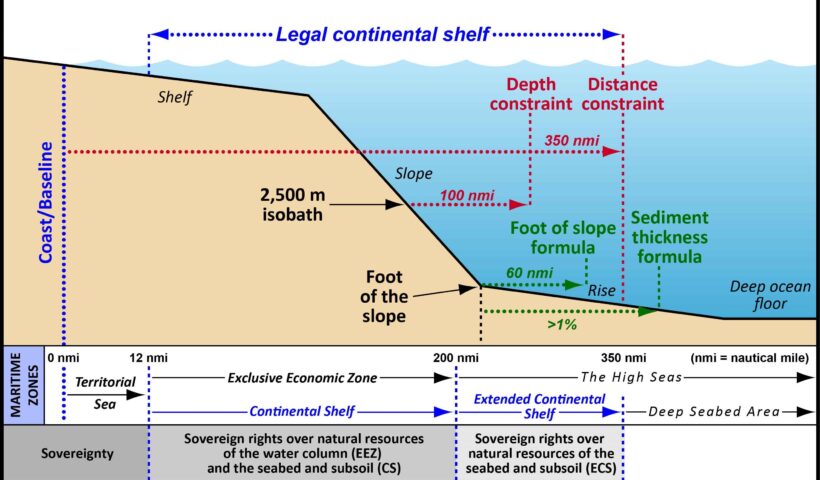
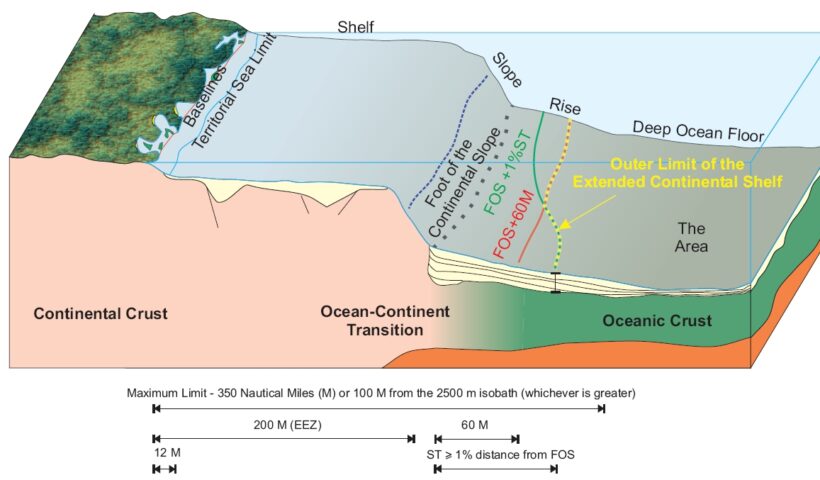
As we shall discuss later, the coastal State intending to claim a continental shelf beyond 200 nautical miles is required to submit information on the limits of the shelf to the Commission. The Commission consists of twenty-one members who shall be experts in the field of geology, geophysics or hydrography. The members of the Commission are to be elected by States Parties to the LOSC from among their nationals, having due regard to the need to ensure equitable geographical representation, and they shall serve in their personal capacities in accordance with Article 2(1) of Annex II…The Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf, duties, authorities and works, Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf, continental shelf, LOSC, What are the characteristics of the continental shelf?, What does continental slope mean?, What extended continental shelf?, What is continental shelf limit?, What is the importance of continental shelf?, What is the largest continental shelf?, Where is the continental shelf?
View More The Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf, duties, authorities and worksCriteria for Determining the Outer Limits of the Continental Shelf Beyond 200 Nautical Miles(extended continental shelf (ECS))
Where the outer edge of the continental margin extends beyond 200 nautical miles, the limit of the continental shelf is to be determined on the basis of the geological criteria set out by Article 76(4). This provision contains two criteria for fixing the seaward limit of the continental shelf.
View More Criteria for Determining the Outer Limits of the Continental Shelf Beyond 200 Nautical Miles(extended continental shelf (ECS))what is the meaning of CONTINENTAL SHELF on the law of the sea and customary international law?
In light of the dictum of the Court and Article 76 of the LOSC, it may be argued that currently the distance criterion is the legal title over the continental shelf up to 200 nautical miles, and the natural prolongation offers legal title over the shelf beyond 200 nautical miles. what is the meaning of CONTINENTAL SHELF on the law of the sea and customary international law?, Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf, continental shelf, Continental Shelf Beyond 200 Nautical Miles, extended continental shelf, LOSC, 200 metres isobath, 200 nautical miles, Article 76 of the LOSC, continent, continental shelf, Convention on the Continental Shelf, LOSC, North Sea Continental Shelf cases, seabed, submarine, subsoil, Truman Proclamation
View More what is the meaning of CONTINENTAL SHELF on the law of the sea and customary international law?Historic Rights of countries on the EEZ, based on law of the sea and customary international law
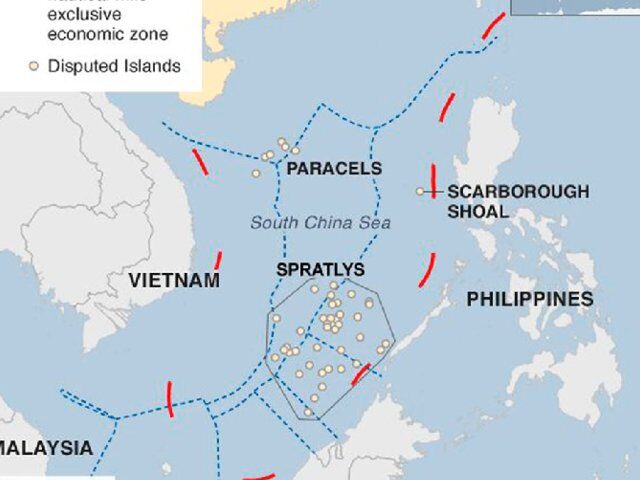
Historic Rights of countries on the EEZ, based on law of the sea and customary international law, EEZ, exclusive economic zone, High seas, historic rights, LOSC, south china sea
View More Historic Rights of countries on the EEZ, based on law of the sea and customary international lawResidual Rights of countries on the EEZ based on law of the sea and customary international law
Residual Rights of countries on the EEZ based on law of the sea and customary international law, EEZ, exclusive economic zone, LOSC, Residual Rights
View More Residual Rights of countries on the EEZ based on law of the sea and customary international lawFreedoms of Third States activity on the EEZ, based on the law of the sea and customary international law
Freedoms of Third States activity on the EEZ, based on the law of the sea and customary international law, coastal State jurisdiction in the EEZ, freedom of laying submarine cables, LOSC, Third States activity on the EEZ
View More Freedoms of Third States activity on the EEZ, based on the law of the sea and customary international lawJurisdiction of Coastal States Over the EEZ, based on law of the sea, customary international law and LOSC
Jurisdiction of Coastal States Over the EEZ, based on law of the sea, customary international law and LOSC, artificial islands, EEZ, exclusive economic zone, IMO, ITLOS, LOSC
View More Jurisdiction of Coastal States Over the EEZ, based on law of the sea, customary international law and LOSCLegal Status of the EEZ at LOSC, law of the sea and customary international law
In short, unlike territorial sovereignty, the sovereign rights of the coastal State over the EEZ lack comprehensiveness of material scope. With respect to matters accepted by international law, however, the coastal State can exercise both legislative and enforcement jurisdiction over all people within the EEZ in an exclusive manner. The essential point is that the rights of the coastal State over the EEZ are spatial in the sense that they can be exercised solely within the particular space in question regardless of the nationality of persons or vessels. Thus the coastal State jurisdiction over the EEZ can be regarded as a spatial jurisdiction. Due to the lack of comprehensiveness of material scope, this jurisdiction should be called a limited spatial jurisdiction.. Legal Status of the EEZ at LOSC, law of the sea and customary international law, coastal State, EEZ, ITLOS, Legal Status of the EEZ, limitation ratione materiae, LOSC, ratione materiae, ratione personae, Sovereign Rights Over the EEZ
View More Legal Status of the EEZ at LOSC, law of the sea and customary international lawwhat is the meaning of EXCLUSIVE ECONOMIC ZONE (treaties and customary international law)
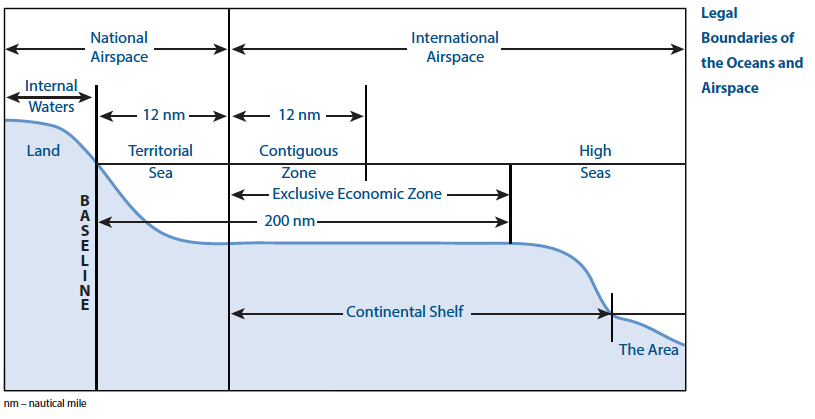
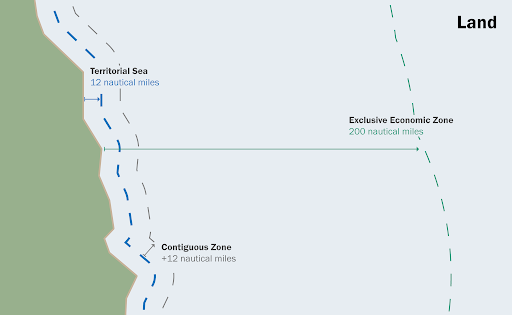
The EEZ is an area beyond and adjacent to the territorial sea, not extending beyond 200 nautical miles from the baseline of the territorial sea. The origin of the concept of the EEZ may go back to the practice of the Latin American States after World War II. Originally the figure of 200 nautical miles appeared in 1947, when Chile (23 June 1947) and Peru (1 August 1947) claimed such an extent for the exercise of full sovereignty. The figure of 200 nautical miles relied on scientific facts: it would enable the Andean States to reach the Peruvian and the Humboldt Currents, which were particularly rich in living species.
.. what is the meaning of EXCLUSIVE ECONOMIC ZONE (treaties and customary international law), customary law, Declaration of Santo Domingo, EEZ, exclusive economic zone, maritime zone, Montevideo Declaration, patrimonial sea, sovereignty, UNCLOS I, UNCLOS II, UNCLOS III
CONTIGUOUS ZONE at the sea, in customary international law and LOSC
The Concept of the Contiguous Zone
The contiguous zone is a marine space contiguous to the territorial sea, in which the coastal State may exercise the control necessary to prevent and punish infringement of its customs, fiscal, immigration or sanitary laws and regulations within its territory or territorial sea. . CONTIGUOUS ZONE at the sea, in customary international law and LOSC, Concept of the Contiguous Zone, contiguous zone, EEZ, enforcement jurisdiction in its contiguous zone, High seas
Rights and Obligations of an Archipelagic State in law of the sea, customary international law and LOSC
Article 44 of the LOSC applies mutatis mutandis to archipelagic sea lanes passage. It follows that archipelagic States shall not hamper archipelagic sea lanes passage and shall give appropriate publicity to any danger to navigation or overflight within or over the strait of which they have knowledge. In addition to this, there shall be no suspension of archipelagic sea lanes passage..Rights and Obligations of an Archipelagic State in law of the sea, customary international law and LOSC, Archipelagic Sea Lanes Passage, archipelagic State, Article 44 of the LOSC
View More Rights and Obligations of an Archipelagic State in law of the sea, customary international law and LOSCThe Right of Archipelagic Sea Lanes Passage based on law of the sea(and customary international law and LOSC)
The principal elements of the right of archipelagic sea lanes passage can be summarised:
(i) As with the right of transit passage, the right of archipelagic passage applies between one part of the high seas or an EEZ and another part of the high seas or an EEZ.
(ii) All ships and aircraft enjoy the right of archipelagic sea lanes passage in such sea lanes and air routes under Article 53(2). The right of archipelagic sea lanes passage contains the rights of overflight by aircraft. In common with the right of transit passage, foreign warships and military aircraft have the right of archipelagic sea lanes passage.
(iii) Like the right of transit passage, archipelagic sea lanes passage must be the exercise of the rights of navigation and overflight solely for the purpose of continuous, expeditious and unobstructed transit. The Right of Archipelagic Sea Lanes Passage based on law of the sea(and customary international law and LOSC), air routes, Archipelagic Sea Lanes Passage, archipelagic State, IMO, Marine Safety Committee, territorial sea
The Right of Innocent Passage Through Archipelagic Waters(in law of the sea, customary international law and LOSC)
The Right of Innocent Passage Through Archipelagic Waters(in law of the sea, customary international law and LOSC), delimitation of internal waters, Innocent Passage, Innocent Passage Through Archipelagic Waters, submarines, territorial sea, underwater vehicles
View More The Right of Innocent Passage Through Archipelagic Waters(in law of the sea, customary international law and LOSC)Jurisdiction of Archipelagic States Over Archipelagic Waters(based on law of the sea, customary international law and LOSC)
As clearly stated in Article 49(1) and (2) of the LOSC, archipelagic waters are under the territorial sovereignty of the archipelagic State. However, care should be taken in noting that the exercise of the archipelagic State’s territorial sovereignty is subject to general international law and specific provisions under Part IV of the LOSC.. Jurisdiction of Archipelagic States Over Archipelagic Waters(based on law of the sea, customary international law and LOSC), archipelagic doctrine, Archipelagic States, Archipelagic States and Maritime Navigation, archipelagic waters, Archipelagic Waters and Exclusive Economic Zone, archipelagic waters unclos, archipelagic waters vs internal waters, Duzgit Integrity Arbitration, Jurisdiction of Archipelagic States, Legal status of archipelagic waters, LOSC, The Archipelagic States Concept, What are the four categories of waters under the Unclos?, What is archipelagic baseline?, What is the archipelagic rule?, Which waters are identified as archipelagic waters?
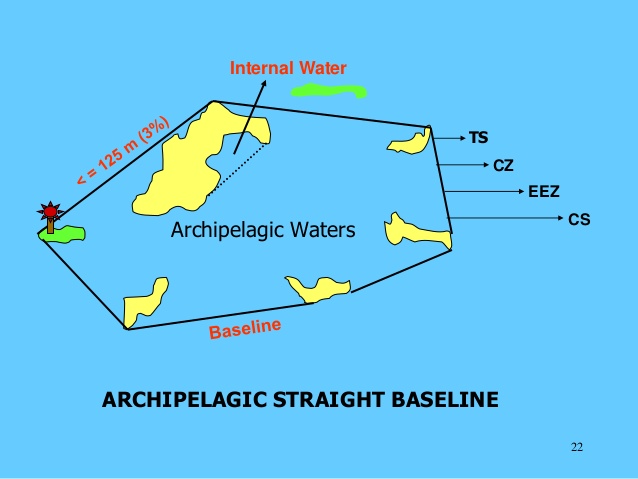
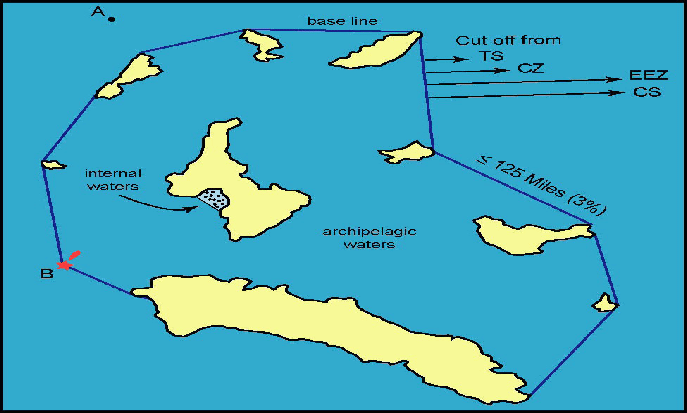
View More Jurisdiction of Archipelagic States Over Archipelagic Waters(based on law of the sea, customary international law and LOSC)how draw Archipelagic Baselines in the international law of the sea and LOSC?
Article 47(1) of the LOSC provides as follows :
An archipelagic State may draw straight archipelagic baselines joining the outermost points of the outermost islands and drying reefs of the archipelago.
A key point is that the legal criteria of being an archipelago must be fulfilled in order to construct archipelagic baselines. In other words, a State which does not meet the legal definition of an archipelagic State is not entitled to draw archipelagic baselines. The language of this provision also suggests that the establishment of archipelagic baselines is facultative. Article 47 sets out conditions for drawing these baselines in some detail… how draw Archipelagic Baselines in the international law of the sea and LOSC?, Archipelagic Baselines, archipelagic State, High seas, LOSC, low-tide elevations, opinio juris, straight archipelagic baselines, territorial sea
what is the meaning ARCHIPELAGIC WATERS in the international law of the sea and LOSC?
The key concept of archipelagic waters is that a group of islands in mid-ocean, i.e. ‘midocean archipelagos’, should be considered as forming a unit; and that the waters enclosed by baselines joining the outermost points of the archipelago should be under territorial sovereignty. While the question of a special archipelagic regime has been discussed on various occasions since the early twentieth century, neither the 1930 Hague Conference, nor UNCLOS I could resolve this question. The 1958 Geneva Conventions contain no provision with regard to mid-ocean archipelagos or archipelagic waters.
. what is the meaning ARCHIPELAGIC WATERS in the international law of the sea and LOSC?, archipelagic doctrine, Archipelagic States and Maritime Navigation, archipelagic waters, Archipelagic Waters and Exclusive Economic Zone, archipelagic waters unclos, archipelagic waters vs internal waters, archipelago, Article 46(a) of the LOSC, continental shelf, EEZ, law of the sea, Legal status of archipelagic waters, LOSC, The Archipelagic States Concept, UNCLOS I, UNCLOS III, What are the four categories of waters under the Unclos?, What is archipelagic baseline?, What is the archipelagic rule?, Which countries are archipelagos?, Which waters are identified as archipelagic waters?
Rights and Obligations of Coastal States Bordering Straits based on international law of the sea and customary international law
The coastal State has a right to adopt laws and regulations relating to transit passage through straits. Under Article 42(1), those laws and regulations involve:
(a) the safety of navigation and the regulation of maritime traffic, as provided in Article 41,
(b) the prevention, reduction and control of pollution, by giving effect to applicable international regulations regarding the discharge of oil, oily wastes and other noxious substances in the strait,
(c) with respect to fishing vessels, the prevention of fishing, including the stowage of fishing gear, and
(d) the loading or unloading of any commodity, currency or person in contravention of the customs, fiscal, immigration or sanitary laws and regulations of States bordering straits. States bordering straits are required to give due publicity to all such laws and regulations in accordance with Article 41(3).
Rights and Obligations of Coastal States Bordering Straits based on international law of the sea and customary international law, Article 43 of the LOSC, coastal State, Coastal States Bordering Straits, environmental protection, Great Belt case between Finland and Denmark, Legality of Creation of Bridges in International Straits, LOSC, MODUs, non-suspendable innocent passage, Torres Strait
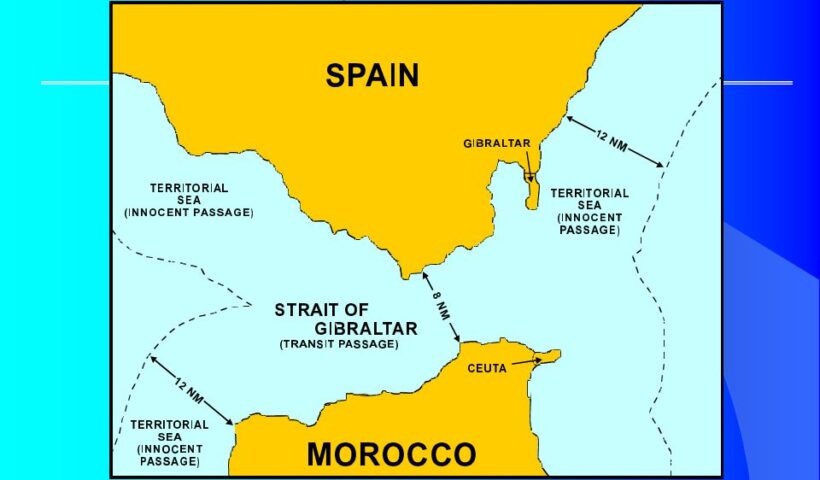
international law of the sea and The Right of Transit Passage on the international straits
Article 38(2) of LOSC defines transit passage as:
the exercise in accordance with this Part [III] of the freedom of navigation and overflight solely for the purpose of continuous and expeditious transit of the strait between one part of the high seas or an exclusive economic zone and another part of the high seas or an exclusive economic zone.
This provision continues that: ‘the requirement of continuous and expeditious transit does not preclude passage through the strait for the purpose of entering, leaving or returning from a State bordering the strait, subject to the conditions of entry to that State’. Thus the transit passage includes lateral and inward/outward-bound passage. The right of transit passage in international straits differs from the right of innocent passage in the territorial sea in four respects.. international law of the sea and The Right of Transit Passage on the international straits, Chicago Convention with respect to the airspace over the straits, continuous and expeditious transit, exclusive economic zone, freedom of navigation, international straits, submarines, transit passage, UNCLOS III
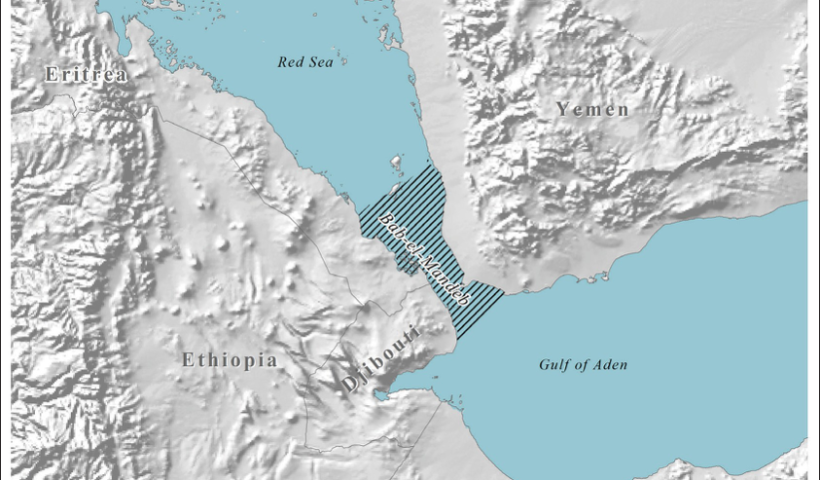
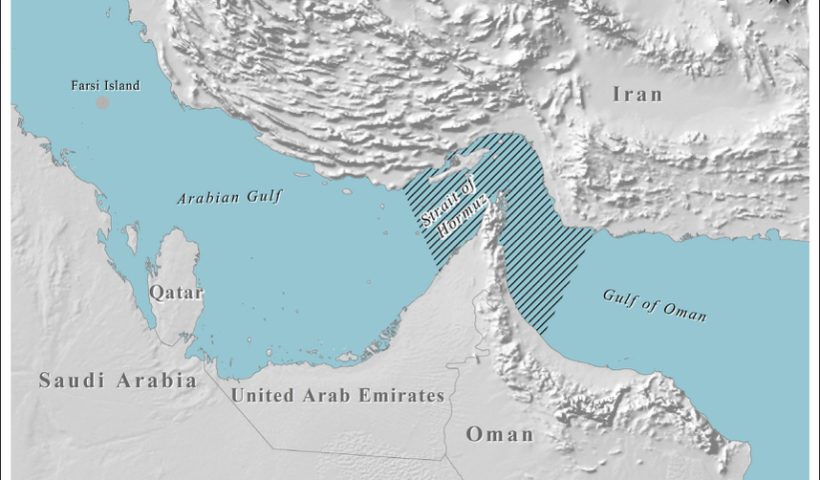
what is the meaning of INTERNATIONAL STRAITS and its legal issues (typology and rules)
The straits under Part III of the LOSC contain two types of straits: straits to which the regime of transit passage applies and straits to which the right of innocent passage applies.
The first type concerns straits to which the regime of transit passage applies. In this regard, Article 37 provides: This section applies to straits which are used for international navigation between one part of the high seas or an exclusive economic zone and another part of the high seas or an exclusive economic zone. This provision contains two criteria for identifying international straits under Part III.
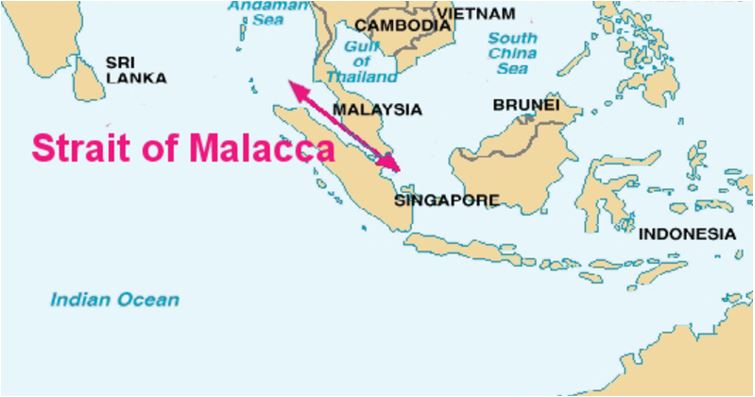
The first is the geographical criterion. Such straits are those connecting ‘one part of the high seas or an exclusive economic zone and another part of the high seas or an exclusive economic zone’. The second is the functional criterion, namely ‘straits used for international navigation’. Concerning the relationship between the two criteria, the ICJ, in the Corfu Channel case, seemed to consider that the geographical criterion provided the primary criterion… what is the meaning of INTERNATIONAL STRAITS and its legal issues (typology and rules), Åland Islands, Åland Strait, archipelagic waters, Arctic Ocean, Arctic waters, Article 36 of the LOSC, Atlantic Oceans, Corfu Channel judgment, Dardanelles, Dover Strait, EEZ, international navigation, international shipping, international straits, LOSC, Montreux Convention, non-suspendable innocent passage, Osumi Strait, right of innocent passage, Strait of Gibraltar, Strait of Magellan, Straits of Malacca, territorial sea, territorialisation, transit passage, Turkish Straits
The Obligations of the Coastal State Concerning Innocent Passage (treaties and customary international law)
In light of the importance of sea communication for all States, the LOSC places certain obligations upon the coastal State to ensure the interests of navigation in its territorial sea.
First, under Article 24(1) of the LOSC, the coastal State is obliged not to hamper the innocent passage of foreign ships and not to discriminate in form or in fact against the ships of any State or against ships carrying cargoes to, from or on behalf of any State.
Second, the coastal State is under the obligation to give appropriate publicity to any danger to navigation under Article 24(2). This obligation follows from the dictum in the Corfu Channel judgment.
Third, no charge may be levied upon foreign ships by reason only of their passage through the territorial sea pursuant to Article 26.. The Obligations of the Coastal State Concerning Innocent Passage (treaties and customary international law), Article 24(1) of the LOSC, coastal State, Corfu Channel judgment, Innocent Passage
The Rights of the Coastal State Concerning Innocent Passage (treaties and customary international law)
The Rights of the Coastal State Concerning Innocent Passage (treaties and customary international law), 22 and 25 of the LOSC, Article 28 of the LOSC, Articles 21, coastal State, coastal States, flag State, illicit traffic in narcotic drugs, immigration or sanitary laws, Innocent Passage, maritime traffic, navigational aids and facilities, prevention of infringement of the customs, protection of cables and pipelines, territorial sea
View More The Rights of the Coastal State Concerning Innocent Passage (treaties and customary international law)The Right of Innocent Passage of Foreign Nuclear-Powered Ships and Ships Carrying Inherently Dangerous or Noxious Substances
The Right of Innocent Passage of Foreign Nuclear-Powered Ships and Ships Carrying Inherently Dangerous or Noxious Substances, Article 23 of the LOSC, Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships, EEZ, International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS), Nuclear-Powered Ships, radioactive, radiotoxic nuclear materials, Ships Carrying Inherently Dangerous or Noxious Substances, SOLAS
View More The Right of Innocent Passage of Foreign Nuclear-Powered Ships and Ships Carrying Inherently Dangerous or Noxious SubstancesThe Right of Innocent Passage of Warships in the law of the sea ( convention, practice and customary international law)
The Right of Innocent Passage of Warships in the law of the sea ( convention, practice and customary international law), Article 17 of the LOSC, Article 20 of the LOSC, ICJ, Innocent Passage, submarines, The Right of Innocent Passage, Warships
View More The Right of Innocent Passage of Warships in the law of the sea ( convention, practice and customary international law)what is “The Right of Innocent Passage” in law of the sea and customary international law
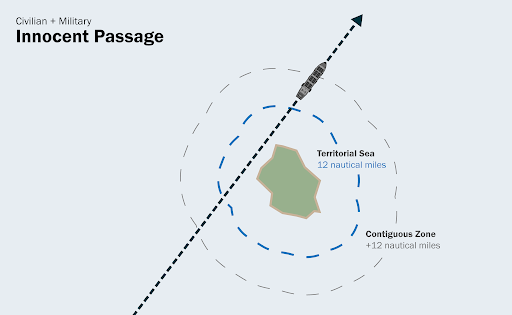
The right of innocent passage through the territorial sea is based on the freedom of navigation as an essential means to accomplish freedom of trade. In his book published in 1758, Emer de Vattel had already accepted the existence of such a right. Subsequently, in the Twee Gebroeders case of 1801, Lord Stowell ruled that: ‘[T]he act of inoffensively passing over such portions of water, without any violence committed there, is not considered as any violation of territory belonging to a neutral state – permission is not usually required.’ It may be considered that the right of innocent passage became established in the middle of the nineteenth century. In this regard, the Report Adopted by the Committee on 10 April 1930 at the Hague Conference for the Codification of International Law clearly stated:
This sovereignty [over the territorial sea] is, however, limited by conditions established by international law; indeed, it is precisely because the freedom of navigation is of such great importance to all States that the right of innocent passage through the territorial sea has been generally recognised. what is “The Right of Innocent Passage” in law of the sea and customary international law, 1972 Convention on the International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea, Article 17 of the LOSC, Article 19(2) of the LOSC, coastal State, coastal States, fishing activities, Innocent Passage, landing or taking on board of any aircraft, Lord Stowell, serious pollution, spying, territorial sea, The Right of Innocent Passage, Twee Gebroeders case, underwater vehicles
Legal Status of the Territorial Sea (international law of the sea, LOSC, cases)
The territorial sea is a marine space under the territorial sovereignty of the coastal State up to a limit not exceeding 12 nautical miles measured from baselines. The territorial sea comprises the seabed and its subsoil, the adjacent waters, and its airspace. The landward limit of the territorial sea is the baseline. In the case of archipelagic States, the inner limit of the territorial sea is the archipelagic baseline. The outer limit of the territorial sea is the line every point of which is at a distance from the nearest point of the baseline equal to the breadth of the territorial sea.. Legal Status of the Territorial Sea (international law of the sea, LOSC, cases), 12-nautical-mile territorial sea, 1909 Grisbadara case, Article 2(3) of the LOSC, Legal Status of the Territorial Sea, LOSC, territorial sea, territorial waters
View More Legal Status of the Territorial Sea (international law of the sea, LOSC, cases)international law of the sea and Ships in Distress at Sea
international law of the sea and Ships in Distress at Sea, Article 195 of the LOSC, jus cogens, M/V Toledo judgment, opinio juris, Rights of Ships in Distress, Ships in Distress at Sea
View More international law of the sea and Ships in Distress at SeaAccess to Ports in the international law of the sea(internal water)
Access to Ports in the international law of the sea(internal water), 1923 Geneva Convention and Statute on the International Regime of Maritime Ports, Access to Ports, internal waters, Nicaragua case
View More Access to Ports in the international law of the sea(internal water)Jurisdiction of the Coastal State Over Foreign Vessels in Internal Waters in the law of the sea and LOSC
Normally the civil jurisdiction of the coastal State is not exercised in connection with disputes of a private nature arising between members of the crew. In relation to criminal jurisdiction, international lawyers have been accustomed to contrasting the Anglo-American position with the French position.
Jurisdiction of the Coastal State Over Foreign Vessels in Internal Waters in the law of the sea and LOSC, Article 32 of the LOSC, Jurisdiction of the Coastal State, The 2012 ARA Libertad case
Legal Status of Internal Waters in the law of the sea and LOSC
Legal Status of Internal Waters in the law of the sea and LOSC, Article 5(2) of the TSC, Article 8 of the LOSC, Legal Status of Internal Waters, LOSC
View More Legal Status of Internal Waters in the law of the sea and LOSC