Our ocean and coasts affect us all—even those of us who don’t live near the shoreline. Consider the economy. Through the fishing and boating industry, tourism and recreation, and ocean transport, one in six U.S. jobs is marine-related. Coastal and marine waters support over 28 million jobs. U.S. consumers spend over $55 billion annually for fishery products. Then there’s travel and tourism. Our beaches are a top destination, attracting about 90 million people a year. Our coastal areas generate 85 percent of all U.S. tourism revenues. And let’s not forget about the Great Lakes—these vast bodies of water supply more than 40 million people with drinking water. Our ocean, coasts, and Great Lakes serve other critical needs, too—needs that are harder to measure, but no less important—such as climate regulation, nutrient recycling, and maritime heritage. Last but not least, a healthy ocean and coasts provide us with resources we rely on every day, ranging from food, to medicines, to compounds that make our peanut butter easier to spread! So what does all of this have to do with human health?
View More What does the ocean have to do with human health?Category: Uncategorized
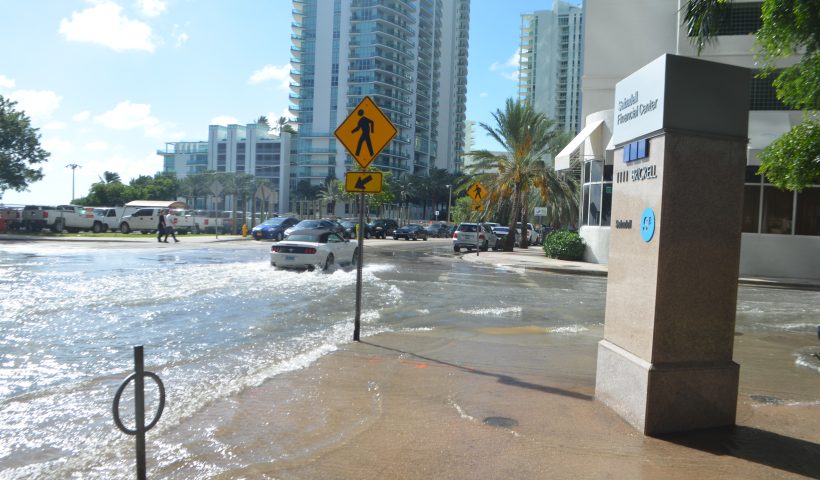
What is high tide flooding?
High tide flooding—flooding that leads to public inconveniences such as road closures—is increasingly common as coastal sea levels rise.
View More What is high tide flooding?What is eutrophication?
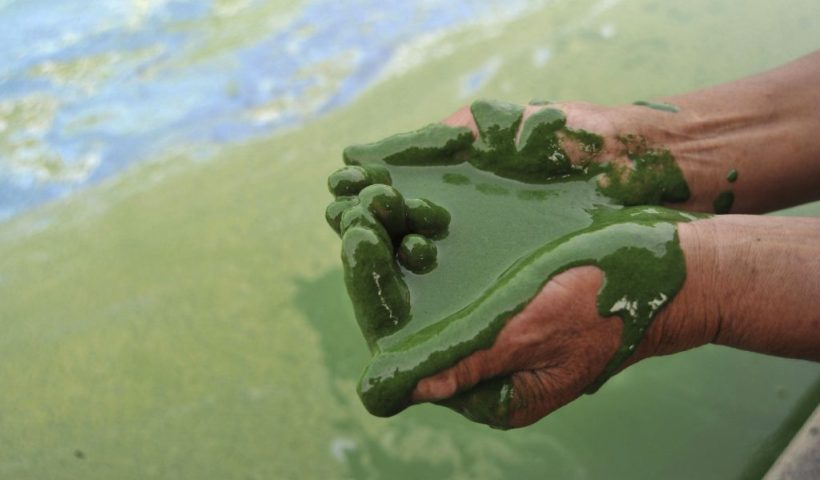
Eutrophication is a big word that describes a big problem in the nation’s estuaries. Harmful algal blooms, dead zones, and fish kills are the results of a process called eutrophication—which begins with the increased load of nutrients to estuaries and coastal waters.
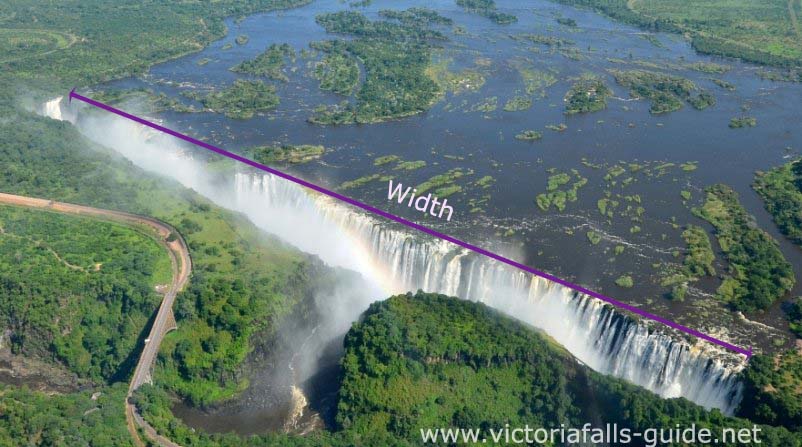
View More What is eutrophication?Where is Earth’s Largest Waterfall?
Rivers flowing over Earth’s gorges create waterfalls that are natural wonders, drawing millions of visitors to their breathtaking beauty, grandeur, and power. But no waterfall is larger or more powerful than those that lie beneath the ocean, cascading over immense cataracts hidden from our view.
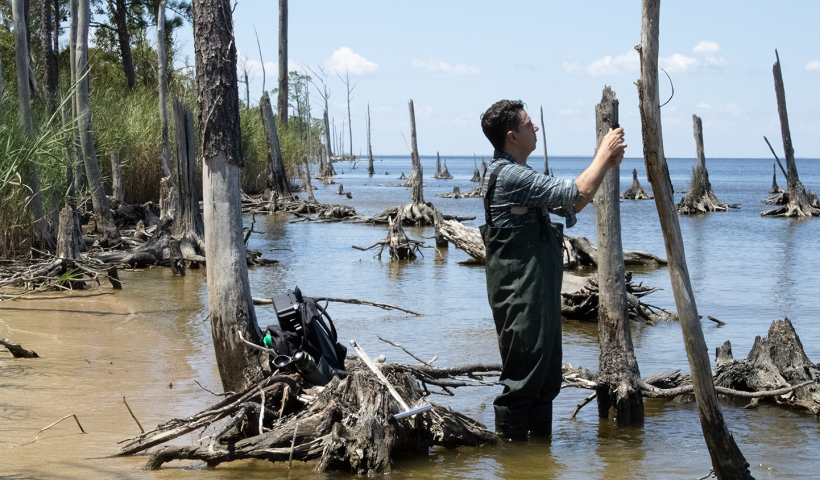
View More Where is Earth’s Largest Waterfall?What is a ghost forest?
As sea level rises, more and more saltwater encroaches on the land. Along the world’s coasts and estuaries, invading seawater advances and overtakes the fresh water that deciduous trees rely upon for sustenance. The salty water slowly poisons living trees, leaving a haunted ghost forest of dead and dying timber. Still standing in or near brackish water, the decaying trees of a ghost forest resemble giant graying pillars that protrude into the air.
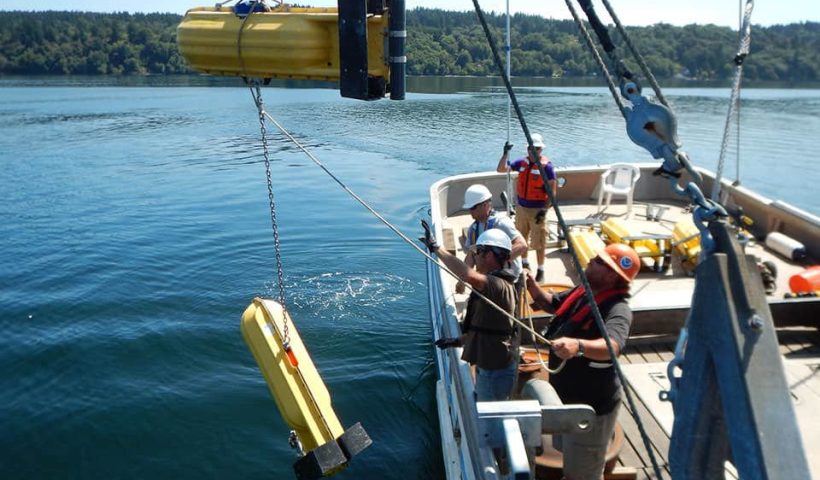
View More What is a ghost forest?What is a current survey?
NOAA’s Center for Operational Oceanographic Products and Services provides tidal current predictions to commercial and recreational mariners who rely on this information for safe navigation. In order to provide the most accurate predictions possible, NOAA must periodically resurvey various coastal and estuarine locations. Survey locations are selected based on mariners’ navigation needs, oceanographic analyses, and the amount of time that has passed since the last survey. Given modern improvements in measurement and computing technology, these surveys greatly improve the accuracy of tidal predictions. In 2017, for example, NOAA concluded a three-year current survey of Puget Sound, Washington, to update the region’s tidal current predictions. Prior to the survey, predictions were based on limited amounts of data collected in the 1930s-1960s.
View More What is a current survey?What is a watershed?
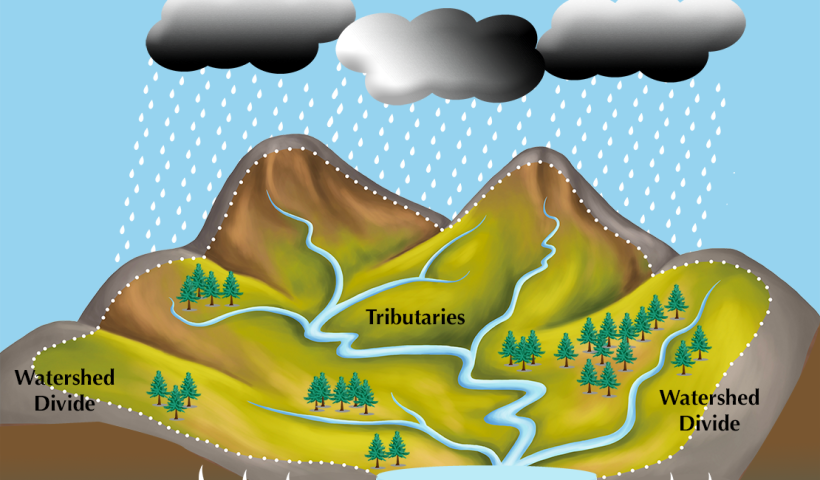
The size of a watershed (also called a drainage basin or catchment) is defined on several scales—referred to as its Hydrologic Unit Codes (HUC)—based on the geography that is most relevant to its specific area. A watershed can be small, such as a modest inland lake or a single county.
View More What is a watershed?What is a meteotsunami?
Meteotsunamis are large waves that scientists are just beginning to better understand. Unlike tsunamis triggered by seismic activity, meteotsunamis are driven by air-pressure disturbances often associated with fast-moving weather events, such as severe thunderstorms, squalls, and other storm fronts. The storm generates a wave that moves towards the shore, and is amplified by a shallow continental shelf and inlet, bay, or other coastal feature.
View More What is a meteotsunami?What is a gyre?
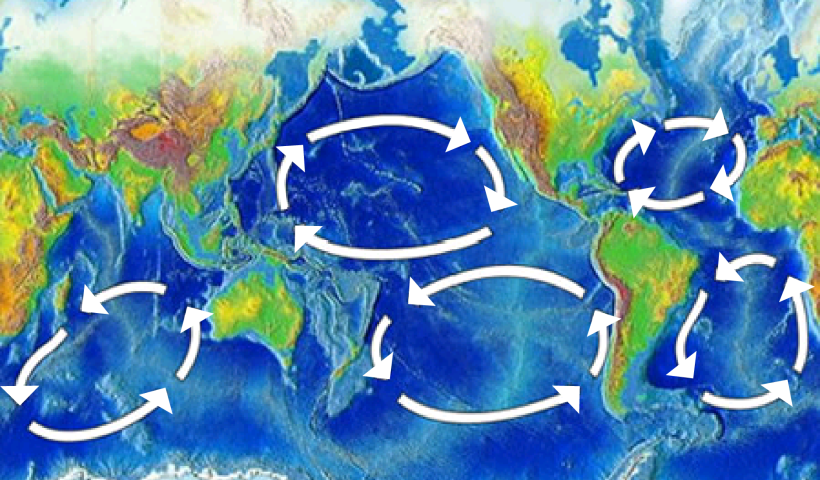
Wind, tides, and differences in temperature and salinity drive ocean currents. The ocean churns up different types of currents, such as eddies, whirlpools, or deep ocean currents. Larger, sustained currents—the Gulf Stream, for example—go by proper names. Taken together, these larger and more permanent currents make up the systems of currents known as gyres.
View More What is a gyre?What is ecoforecasting?
Ecoforecasts detail how interactions between organisms and their environment may affect ecological phenomena such as animal extinction, the spread of invasive plants and disease, and the health of waterbodies.
View More What is ecoforecasting?What is a hydrophone?
Just as a microphone collects sound in the air, a hydrophone detects acoustic signals under the water. Most hydrophones are based on a special property of certain ceramics that produces a small electrical current when subjected to changes in underwater pressure. When submerged in the ocean, a ceramic hydrophone produces small-voltage signals over a wide range of frequencies as it is exposed to underwater sounds emanating from any direction.
View More What is a hydrophone?How do hurricanes form?
Hurricanes are powerhouse weather events that suck heat from tropical waters to fuel their fury. These violent storms form over the ocean, often beginning as a tropical wave—a low pressure area that moves through the moisture-rich tropics, possibly enhancing shower and thunderstorm activity.
View More How do hurricanes form?What is the Bloop?
“The Bloop” is the given name of a mysterious underwater sound recorded in the 90s. Years later, NOAA scientists discovered that this sound emanated from an iceberg cracking and breaking away from an Antarctic glacier.
View More What is the Bloop?What is a glass sponge?
Glass sponges in the class Hexactinellida are animals commonly found in the deep ocean. Their tissues contain glass-like structural particles, called spicules, that are made of silica (hence their name). Some species of glass sponges produce extremely large spicules that fuse together in beautiful patterns to form a “glass house”—a complex skeleton that often remains intact even after the sponge itself dies. The skeleton of the glass sponge, together with various chemicals, provides defense against many predators. Nonetheless, some starfish are known to feed on these rare creatures of the deep.
View More What is a glass sponge?How do hurricanes affect sea life?
When a storm churns across the ocean, the warm surface waters provide additional moisture and can fuel the storm into a hurricane. As the hurricane grows larger and more potent, it can generate waves as high as 60 feet, tossing and mixing warmer surface waters with the colder, saltier water below. The resulting currents can extend as far as 300 feet/91.5 meters below the surface, wreaking deadly havoc on marine life.
View More How do hurricanes affect sea life?What is a lagoon?
Lagoons are separated from larger bodies of water by sandbars, barrier reefs, coral reefs, or other natural barriers. The word “lagoon” derives from the Italian word laguna, which means “pond” or “lake.”
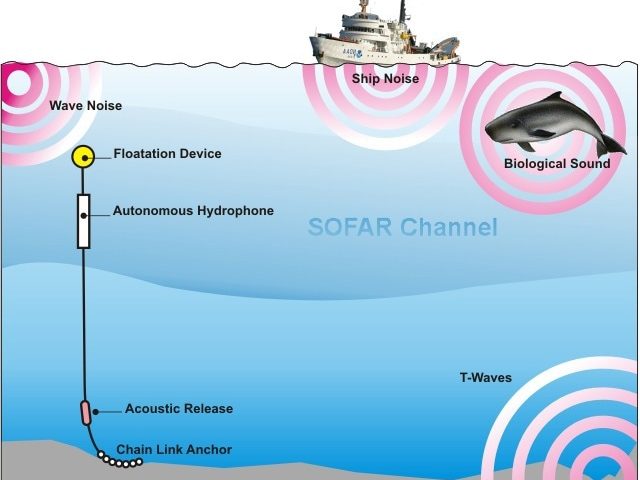
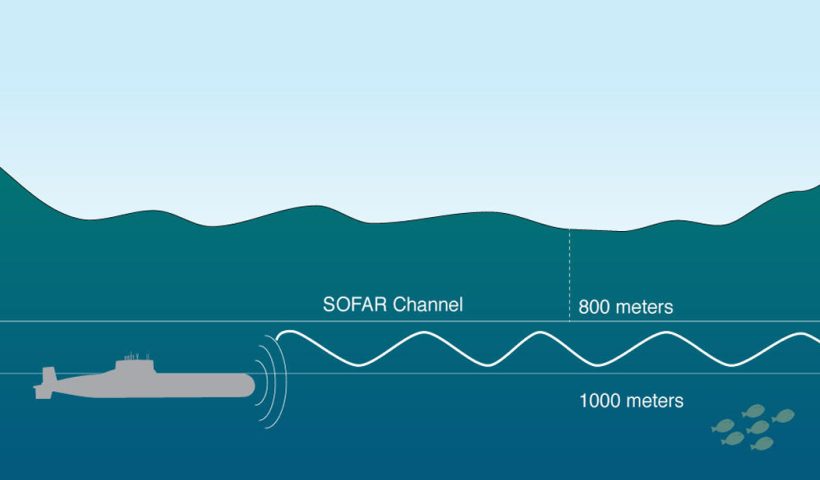
View More What is a lagoon?What is a SOFAR?
How does SOFAR work? Think of the ocean as consisting of various zones, or layers — sort of like oil and vinegar salad dressing before it’s shaken up—except that ocean layers occur due to differences in salinity (salt content) and temperature variations. Saltier water, and colder water, lie beneath less salty, warmer water.
View More What is a SOFAR?How many high tides are there per day?
While some places have one high tide and one low tide per day, most coastal locations have two high tides and two low tides a day. These highs and lows typically aren’t equal. This is why, in most places, using the phrase “high tide” might be unclear. There’s actually high tide and higher high tide (and low and lower low tide).
View More How many high tides are there per day?What do windward and leeward mean?
An island’s windward side faces the prevailing, or trade, winds, whereas the island’s leeward side faces away from the wind, sheltered from prevailing winds by hills and mountains. As trade winds blow across the ocean, they pick up moist air from the water.
View More What do windward and leeward mean?What is a canal?
A canal is a manmade waterway that allows boats and ships to pass from one body of water to another. Canals are also used to transport water for irrigation and other human uses. While the advent of more efficient forms of transportation has reduced the need for canals, they still play a vital role as conduits for transportation and foster global commerce.
View More What is a canal?Do we still need lighthouses?
Though numerous lighthouses still serve seafarers, modern electronic aids to navigation play a larger role in maritime safety in the 21st century.
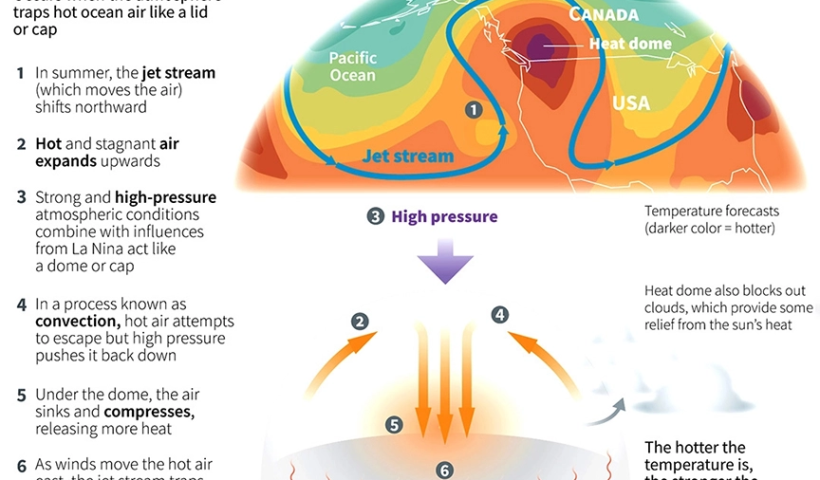
View More Do we still need lighthouses?What is a heat dome?
Summertime means hot weather — sometimes dangerously hot — and extreme heat waves have become more frequent in recent decades. Sometimes, the scorching heat is ensnared in what is called a heat dome. This happens when strong, high-pressure atmospheric conditions combine with influences from La Niña, creating vast areas of sweltering heat that gets trapped under the high-pressure “dome.”
View More What is a heat dome?What causes seasickness?
Seasickness is a result of a conflict in the inner ear, where the human balance mechanism resides, and is caused by a vessel’s erratic motion on the water. Inside the cabin of a rocking boat, for example, the inner ear detects changes in both up-and-down and side-to-side acceleration as one’s body bobs along with the boat. But, since the cabin moves with the passenger, one’s eyes register a relatively stable scene. Agitated by this perceptual incongruity, the brain responds with a cascade of stress-related hormones that can ultimately lead to nausea, vomiting, and vertigo.
View More What causes seasickness?What is the most common form of ocean litter?
Broken bottles, discarded love letters, castoff clothing, candy wrappers, flotsam and jetsam washed ashore: During a walk along a beach, one finds any of these items and more. In all that litter, there is one item more common than any other: cigarette butts.
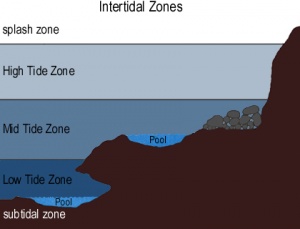
View More What is the most common form of ocean litter?What is the intertidal zone?
Intertidal zones exist anywhere the ocean meets the land, from steep, rocky ledges to long, sloping sandy beaches and mudflats that can extend for hundreds of meters. Four physical divisions, each with distinct characteristics and ecological differences, divide the intertidal zone.
View More What is the intertidal zone?What is a tide pool?
An archipelago is an area that contains a chain or group of islands scattered in lakes, rivers, or the ocean.
View More What is a tide pool?What is a sponge?
Sponges are animals with dense skeletons that are highly adapted to their environments, although it is easy to see why they may be mistaken for…
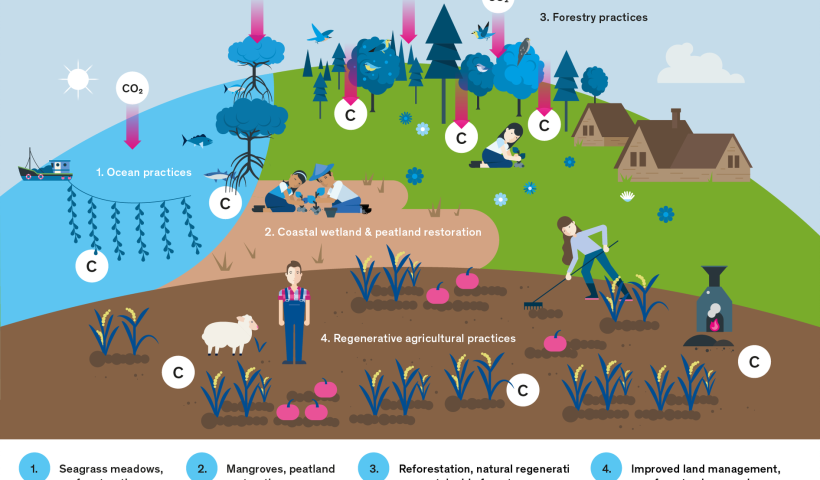
View More What is a sponge?What is the carbon cycle?
Carbon is the foundation of all life on Earth, required to form complex molecules like proteins and DNA. This element is also found in our atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide (CO2). Carbon helps to regulate the Earth’s temperature, makes all life possible, is a key ingredient in the food that sustains us, and provides a major source of the energy to fuel our global economy.
View More What is the carbon cycle?What are coquina and tabby?
Did you know that near St. Augustine, Florida — the nation’s oldest city — there exists an actual “castle” made of sand? Located on 20.5 acres on the western shore of Matanzas Bay, the Castillo de San Marcos National Monument is the oldest (circa 1695) and largest masonry fort in the continental United States.
View More What are coquina and tabby?Can we clean up, stop, or end harmful algal blooms?
Harmful algal blooms — often referred to as HABs for short — occur when algae produce toxic or harmful effects on people, fish, shellfish, marine mammals, birds, or other aquatic organisms. Blooms occur in marine and freshwater environments throughout the world, with damaging ecological, social, and economic effects. So why can’t we clean up the algae and take care of this problem? Unfortunately, the answer is not so simple. Harmful algal blooms are a natural process. There are records of HABs from early European colonists arriving to Florida in the 1500s. However, research points to an increase in the frequency and intensity of algal blooms in modern times due to environmental changes caused by humans.
View More Can we clean up, stop, or end harmful algal blooms?What are plankton?
The word “plankton” comes from the Greek for “drifter” or “wanderer.” An organism is considered plankton if it is carried by tides and currents, and cannot swim well enough to move against these forces. Some plankton drift this way for their entire life cycle. Others are only classified as plankton when they are young, but they eventually grow large enough to swim against the currents. Plankton are usually microscopic, often less than one inch in length, but they also include larger species like some crustaceans and jellyfish.
View More What are plankton?How much oxygen comes from the ocean?
Scientists estimate that 50-80% of the oxygen production on Earth comes from the ocean. The majority of this production is from oceanic plankton — drifting plants, algae, and some bacteria that can photosynthesize. One particular species, Prochlorococcus, is the smallest photosynthetic organism on Earth. But this little bacteria produces up to 20% of the oxygen in our entire biosphere. That’s a higher percentage than all of the tropical rainforests on land combined.
View More How much oxygen comes from the ocean?What is a barrier island?
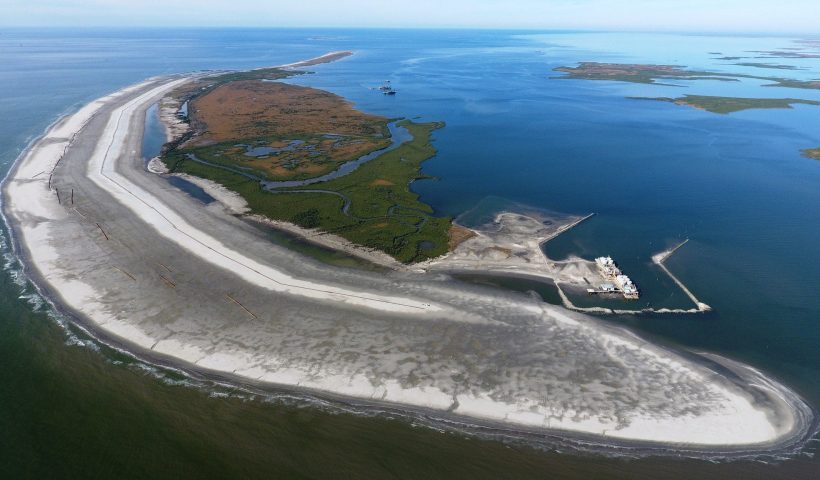
Barrier islands form as waves repeatedly deposit sediment parallel to the shoreline. As wind and waves shift according to weather patterns and local geographic features, these islands constantly move, erode, and grow. They can even disappear entirely.
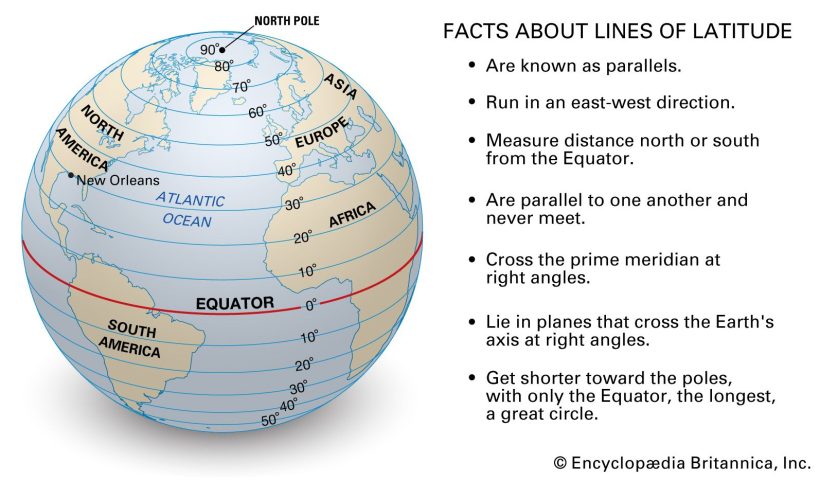
View More What is a barrier island?What is latitude?
Lines of latitude, also called parallels, are imaginary lines that divide the Earth. They run east to west, but measure your distance north or south. The equator is the most well known parallel. At 0 degrees latitude, it equally divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. From the equator, latitude increases as you travel north or south, reaching 90 degrees at each pole.
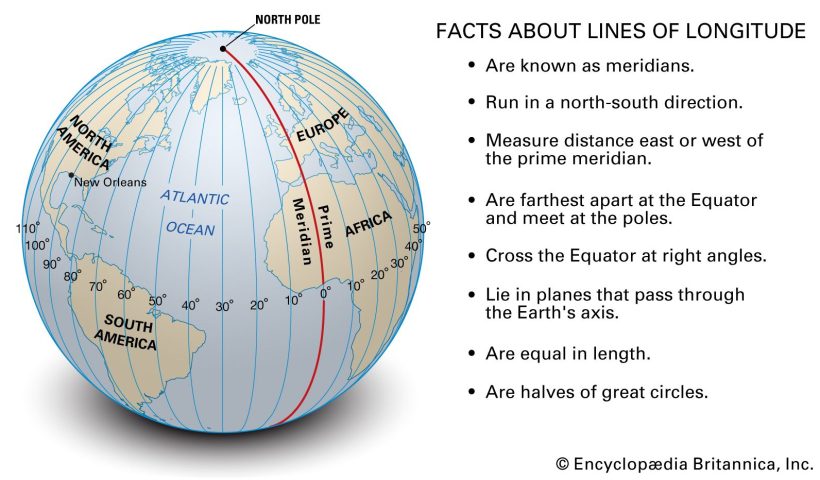
View More What is latitude?What is longitude?
Lines of longitude, also called meridians, are imaginary lines that divide the Earth. They run north to south from pole to pole, but they measure the distance east or west.
View More What is longitude?What are nature-based solutions?
Infrastructure projects that intentionally use natural and nature-based habitats and processes to reduce risks and deliver multiple benefits are referred to as nature-based solutions. Continue…
View More What are nature-based solutions?Boost Your Brand with Sponsor Links: The Ultimate Marketing Hack!
Are you looking for a way to take your brand to new heights? Do you want to dominate the market and stay ahead of the competition? Look no further, because we have the ultimate marketing hack for you – sponsor links! These powerful links have the potential to boost your brand’s visibility, maximize your reach, and transform your marketing strategy. So buckle up and get ready to unleash the power of sponsor links!
View More Boost Your Brand with Sponsor Links: The Ultimate Marketing Hack!Unlocking the Power of Text Links Advertising: How to Boost Your Reach and Revenue
In today’s digital age, advertising has become an integral part of any successful business strategy. As more and more companies are turning to online platforms to promote their products or services, the competition for consumer attention has become fierce. In this highly competitive landscape, it is crucial for businesses to find innovative and effective ways to reach their target audience. One such method that has proven to be highly successful is text link advertising.
View More Unlocking the Power of Text Links Advertising: How to Boost Your Reach and Revenue