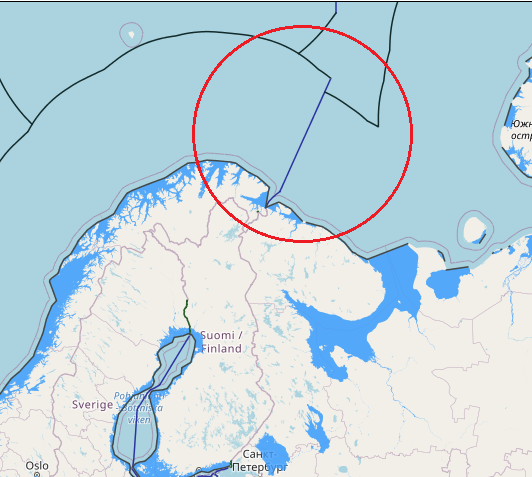
Norway and Russia have delimited their maritime jurisdiction in the maritime areas north of their land boundary. Norway and the former Soviet Union concluded a maritime boundary agreement in 1957 delimiting the territorial sea and continental shelf within Varangerfjorden, a fjord lying seaward of the Norway-Soviet land boundary. The 1957 agreement was superseded by a 2007 agreement between Norway and Russia that delimited the territorial sea, continental shelf, and EEZ in the Varangerfjorden area. This boundary extends from the terminus of the land boundary to an area just seaward of the mouth of Varangerfjorden and is composed of geodetic lines connecting six points, with a total length of approximately 39 M. The agreement contains provisions pertaining to the existence of possible hydrocarbon deposits extending across the boundary line.
Norway and Russia concluded a maritime boundary agreement in 2010 delimiting the EEZ and continental shelf of the two countries in the Barents Sea and Arctic Ocean. The boundary is composed of geodetic lines connecting eight points, with a total length of approximately 907 M. The boundary begins at the terminus of the Varangerfjorden boundary (in the south) agreed in 2007 and terminates in the Arctic Ocean at the point where the last boundary segment (between boundary points 7 and 8) intersects with a line connecting the continental shelf limits of both countries “as established in accordance with Article 76 and Annex II of the Convention.” The 2010 boundary separates the maritime zones generated by the mainland coasts of both countries and also by Svalbard (to the west) and Russia’s Franz Josef Land and Novaya Zemlya (to the east).