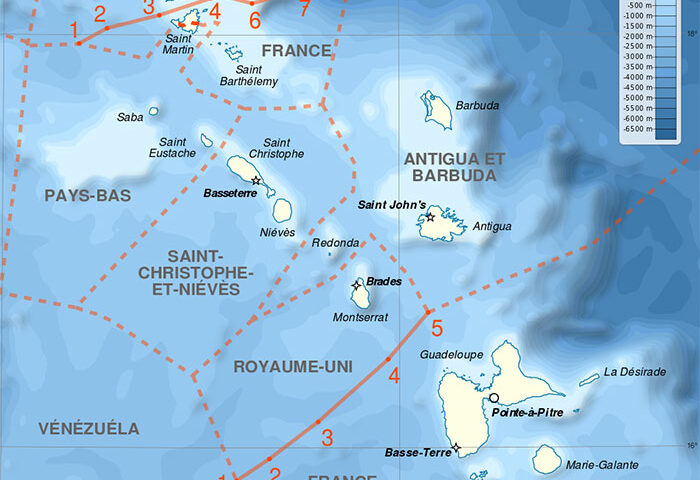
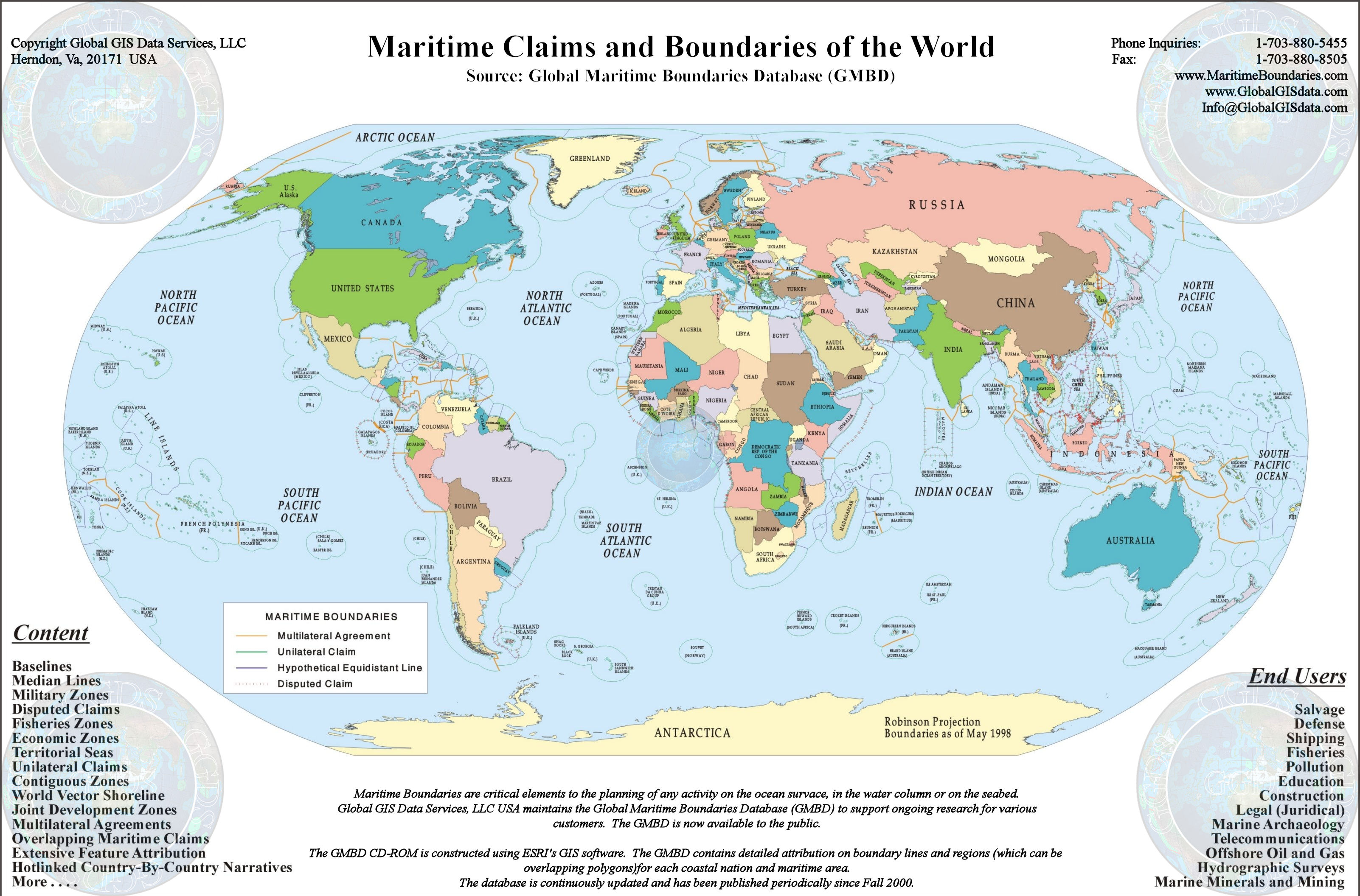
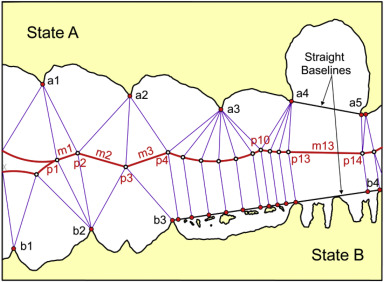
The establishment of continental shelf zones and exclusive economic zones
(EEZs) considerably increased the number and length of the maritime
boundaries between coastal states. A 1983 survey identified some 376
international maritime boundaries between 137 coastal states around the
globe. In 1988, the US Department of State gave a figure of 412 demarcations
required. Eventually, additional boundaries arose due to the advent
of new states and the breaking-up of the Soviet Union. Yet another
generation of boundaries will result from climate change and accessibility
to resources in the Arctic waters.
Tag: What is delimitation of maritime boundary?
Development of the Studies on Maritime Delimitation
Since 1945, in particular, many studies have been written in the field of maritime delimitation. Most of them have focused on the case law. In fact, as is shown in the bibliography, there are many articles relating to international judgments in this field. Since it has been argued that the law of maritime delimitation has developed through international jurisprudence, it was only natural that writers turned to the analysis of case law in this field.
View More Development of the Studies on Maritime DelimitationImportance of Maritime Delimitation in International Law of the Sea
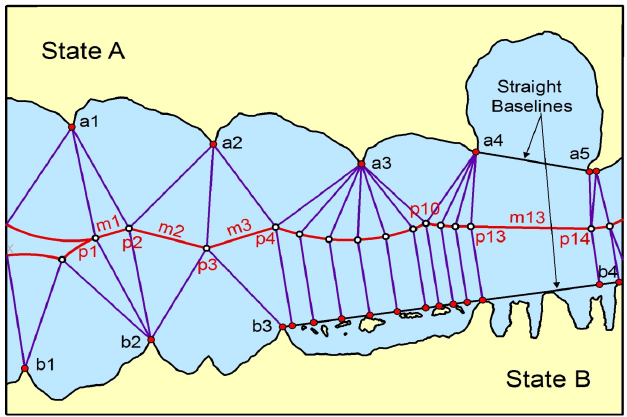
MARITIME SPACES IN international law of the sea are, in essence, defined in relation to the coastal State jurisdiction over each maritime space. Thus, coastal State jurisdiction is the primary criterion in characterising maritime spaces. The ambit of coastal State jurisdiction is in principle defined spatially, based on distance from the coast. According to the 1982 UN Convention on the Law of the Sea, the territorial sea in which a coastal State exercises territorial sovereignty shall not exceed 12 nautical miles measured from the relevant baseline (Article 3). The contiguous zone over which a limited jurisdiction is exercised by the coastal State may not extend beyond 24 nautical miles from that line (Article 33). The Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), where the coastal State may exercise sovereign rights regarding the exploration and exploitation of natural resources, shall not extend beyond 200 nautical miles (Article 57). The same is in principle true for continental shelves of less than 200 nautical miles (Article 76(1)). It would seem safe to say that these rules have now become customary law. Hence, the definition of the spatial extent of coastal State jurisdiction is at the heart of the international law of the sea.
View More Importance of Maritime Delimitation in International Law of the SeaThe Development of the Case Law of Maritime Delimitation: From Equity to Normativity
In parallel with the codification process in the 1958 Geneva Conventions and the 1982 UNCLOS, the law of maritime delimitation was subject to a progressive development through litigation and arbitration. Both processes were at the same time independent and interrelated. The scope of this part is to provide a broad historical background of the evolution of the case law of maritime delimitation in order to better analyze in the following section the conditions, under which the Equidistance/Relevant Circumstances principle had emerged and developed.
View More The Development of the Case Law of Maritime Delimitation: From Equity to NormativityCodification of Maritime Delimitation
The first attempt at codification of the customary law of maritime delimitation started with the 1930 Hague Conference under the auspices of the League of Nations. The Hague Conference failed to reach its purpose and the following World War II period was not an appropriate period to deal with issues of maritime delimitation. In the aftermath of World War II, the creation of the United Nations Organization (UN) and the multiple individual claims of States over maritime spaces, such as the Truman Proclamation and the Santiago Declaration raised the need of re-starting the process of codification of the law of maritime delimitation. The adoption of the 1958 Geneva Conventions which followed was a successful initiative, at least to some extent.
View More Codification of Maritime Delimitationwhat is the meaning of Special Circumstances and Relevant Circumstances in delimitation process at law of the sea
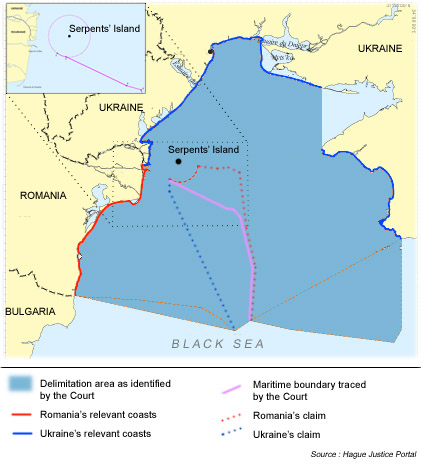
Special circumstances are those circumstances which might modify the results produced by an unqualified application of the equidistance principles. Small islands and maritime features are arguably the archetypical special circumstances as much in the delimitation of the territorial sea as in the delimitation of the continental shelf/EEZ. The Court has recognized in numerous cases, including the North Sea Continental Shelf, Tunisia/Libya, Libya/Malta and Qatar v. Bahrain cases that the equitableness of an equidistance line depends on whether the precaution is taken of eliminating the disproportionate effect of certain islets, rocks and minor coastal projections.
View More what is the meaning of Special Circumstances and Relevant Circumstances in delimitation process at law of the sea