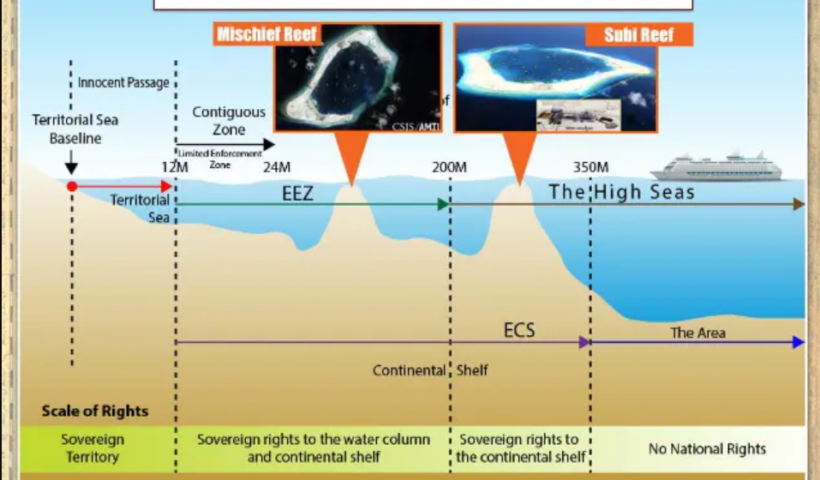
The definition and treatment of islands in maritime boundary delimitation are complex and important. This is because the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), which came into effect in 1994, provides that islands, along with mainland coasts, may generate a full suite of maritime zones – including a 200 nm exclusive economic zone (EEZ) and continental shelf claim as well as a 12 nm territorial sea. Thus, if no maritime neighbours were within 400 nm of the feature, an island has the potential to generate 125,664 sq. nm [431,014 km2] of territorial sea, EEZ and continental shelf rights. There is also the consideration that oceans remain an important source of living resources, with fisheries representing a major industry for many coastal states.
View More difference between islands and rocks in law of the sea
IILSS-International institute for Law of the Sea Studies
law of the sea, LOSC, maritime dispute, maritime law, custom of the sea, maritime claims, maritime boundaries, maritime map, maritime chart