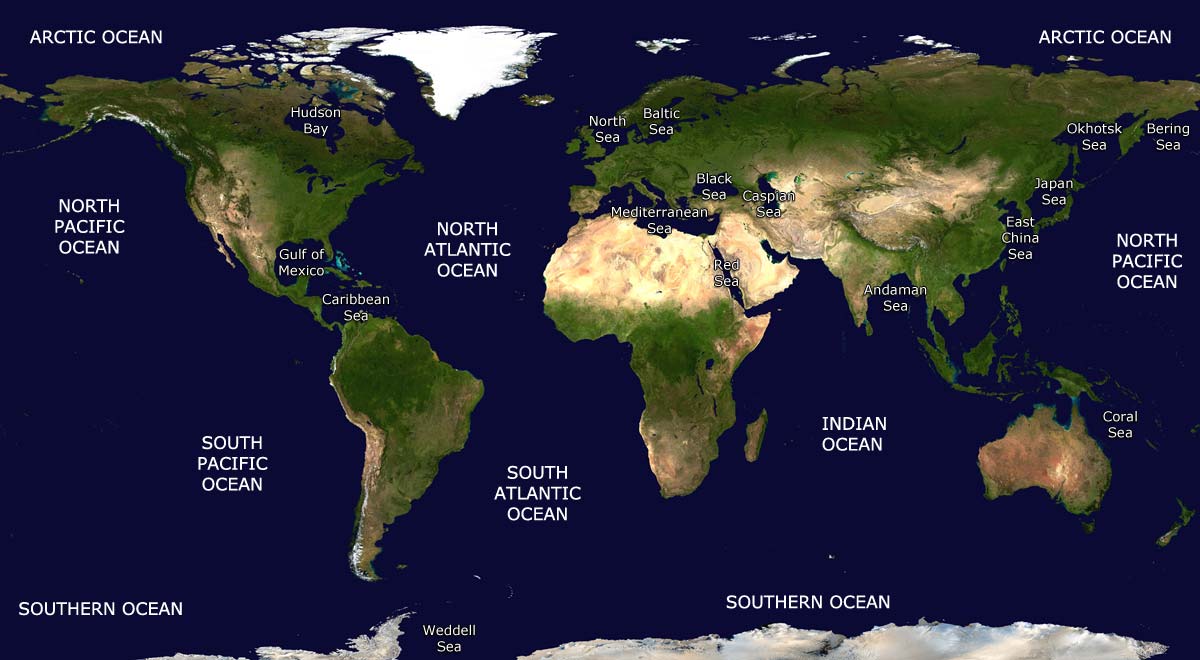
This dataset represents the boundaries of the major oceans and seas of the world. The source for the boundaries is the publication ‘Limits of Oceans & Seas, Special Publication No. 23’ published by the IHO in 1953. The dataset was composed by the Flanders Marine Data and Information Centre.
NB:The Southern Ocean is not included in the IHO publication and its limits are subject of discussion among the scientific community. The Flanders Marine Institute acknowledges the controversy around this subject but decided to include the Southern Ocean in the dataset as this term is often used by scientists working in this area.
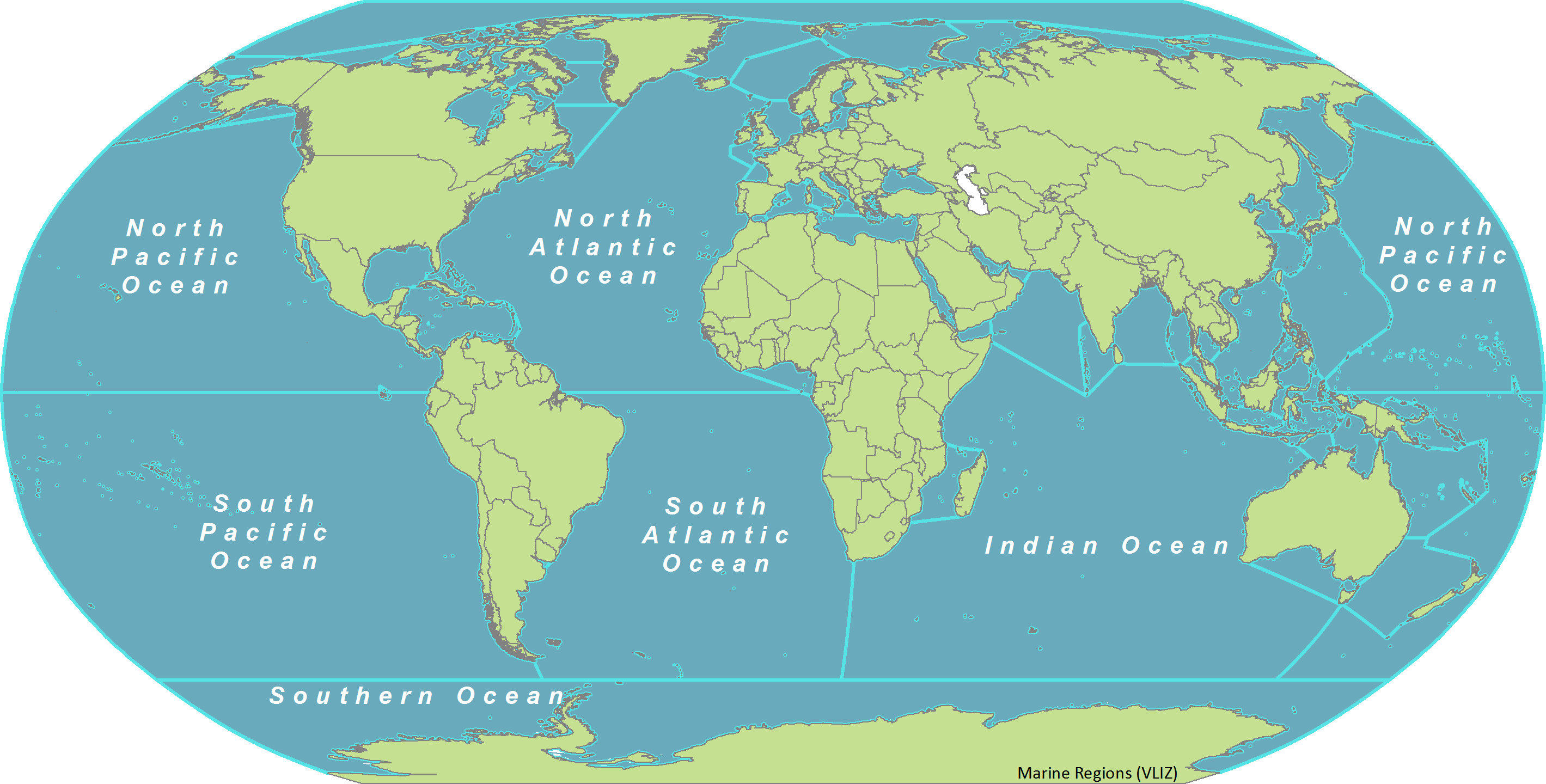
major oceans and seas of the world
While there is only one global ocean, the vast body of water that covers 71 percent of the Earth is geographically divided into distinct named regions. The boundaries between these regions have evolved over time for a variety of historical, cultural, geographical, and scientific reasons.
Historically, there are four named ocean basins: the Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, and Arctic. However, most countries – including the United States – now recognize the Southern (Antarctic) as the fifth ocean basin. The Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian are the most commonly known.
The Southern Ocean is the ‘newest’ named ocean basin. It is recognized by the U.S. Board on Geographic Names as the body of water extending from the coast of Antarctica to the line of latitude at 60 degrees South. The boundaries of this ocean were proposed to the International Hydrographic Organization in 2000. However, not all countries agree on the proposed boundaries, so this has yet to be ratified by members of the IHO.
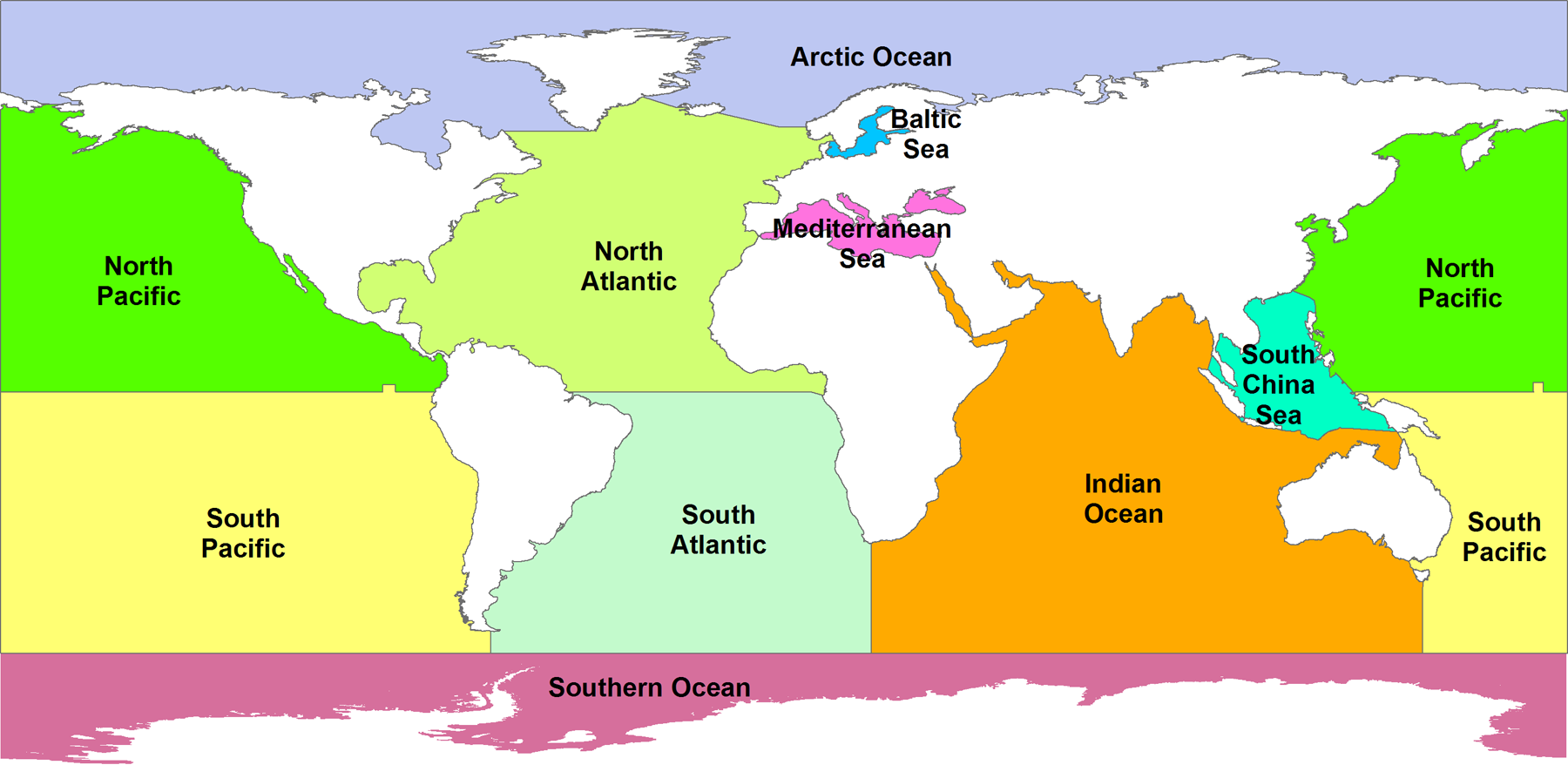

The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water which covers approximately 71% of the surface of the Earth. It is also “any of the large bodies of water into which the great ocean is divided”. A common definition lists five oceans, in descending order by area, the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern (Antarctic), and Arctic Oceans.
Seawater covers approximately 361,000,000 km2 (139,000,000 sq mi) and is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas, with the ocean as a whole covering approximately 71% of Earth’s surface and 90% of the Earth’s biosphere. The world ocean contains 97% of Earth’s water, and oceanographers have stated that less than 20% of the oceans have been mapped. The total volume is approximately 1.35 billion cubic kilometers (320 million cu mi) with an average depth of nearly 3,700 meters (12,100 ft).
As the world’s ocean is the principal component of Earth’s hydrosphere, it is integral to life, forms part of the carbon cycle, and influences climate and weather patterns. The ocean is the habitat of 230,000 known species, but because much of it is unexplored, the number of species in the ocean is much larger, possibly over two million.The origin of Earth’s oceans is unknown; A sizable quantity of water would have been in the material that formed the Earth. Water molecules would have escaped Earth’s gravity more easily when it was less massive during its formation due to atmospheric escape. Oceans are thought to have formed in the Hadean eon and may have been the cause for the emergence of life.
There are numerous environmental issues for oceans which include for example marine pollution, overfishing, ocean acidification and other effects of climate change on oceans. Extraterrestrial oceans may be composed of water or other elements and compounds. The only confirmed large stable bodies of extraterrestrial surface liquids are the lakes of Titan, although there is evidence for oceans’ existence elsewhere in the Solar System.


Britannica said, Earth possesses one “world ocean.” However, those conducting oceanic research generally recognize the existence of five major oceans: the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic, and Southern oceans. Arbitrary boundaries separate these bodies of water. The boundaries of each ocean are largely defined by the continents that frame them. In the Southern Hemisphere the southern portions of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian oceans and their tributary seas that surround Antarctica are often referred to as the Southern Ocean. Many subdivisions can be made to distinguish the limits of seas and gulfs that have historical, political, and sometimes ecological significance. However, water properties, ocean currents, and biological populations are not constrained by these boundaries. Indeed, many researchers do not recognize them either.
Pacific Ocean
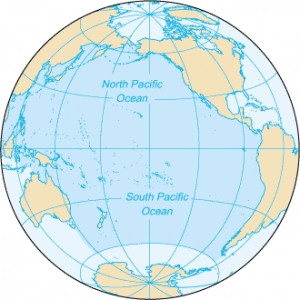
The Pacific Ocean is the largest ocean covering more than 30% of the Earth. This is close to half of the water on Earth. It touches the west coast border of the Americas along with east Asia and Australia. The equator divides the Pacific Ocean into two separate parts – the North Pacific Ocean and South Pacific Ocean. Pacific means “peaceful” in Latin. It has the deepest trenches with an average depth of 3800m.
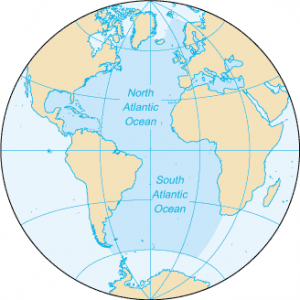
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is situated between the Americas and European/African continents. The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest and saltiest ocean in the world. It resembles an S-shape between the Americas, Europe, and Africa. “Atlantic” originated from the Greek god “Atlas” who carried the sky for eternity. The ocean bottom is composed of mid-Atlantic Ridge. This submarine mountain range extends all the way from Iceland to 58 degrees South latitude. It’s part of the longest mountain range in the world. The Vikings, Portuguese, and Christopher Columbus have extensively explored the Atlantic Ocean. Similarly to this day, it’s being used for trade routes such as the transatlantic trade route.
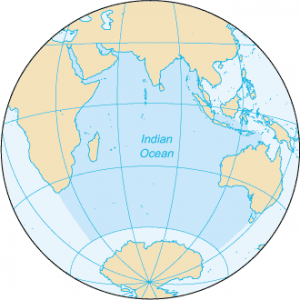
The Indian Ocean is the third largest ocean surrounding a densely populated region. It contains an additional 20% of the water on Earth’s surface. It borders India in the North, East Africa, Australia, and the Southern Ocean. Because of the higher water temperature, it has limited marine life. Since about 800 A.D. the Indian Ocean has played an important role in trading. For centuries, navigators have sailed along major ocean currents for shipment routes. It is bounded by 4 tectonics plate boundaries and may include an additional plate boundary. It is the geologically youngest of the 5 oceans with spreading ridges at divergent plate boundaries.
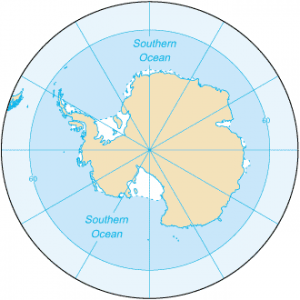
Southern Ocean
In 2000, the Southern Ocean is the newest ocean recognized by the International Hydrographic Organization. It borders Antarctica in its entirety. In terms of size, it’s the fourth-largest at 20,327,000 square kilometers. It extends out to 60 degrees South latitude. It’s an extreme environment and is the least understood of the 5 oceans. This is because it is unexplored, far from populated areas, and has a severe climate. Despite the Southern Ocean being unexplored, about 80% of all oceans in the world are unexplored. There’s still a lot of work to do for ocean exploration.
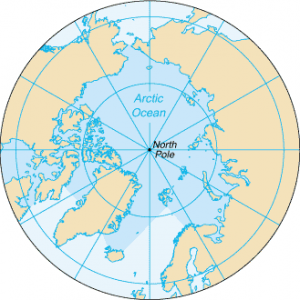
The Arctic Ocean is the world’s smallest and shallowest ocean of all 5 oceans. Further to this, it is the coldest and least salty ocean. In size, the Arctic Ocean is about the size of Russia. Because it’s located at the North Pole, the Arctic Ocean has polar ice. But over the years, glaciers have melted threatening sea levels to rise. Despite the IHO recognizing it as the “Arctic Ocean”, some oceanographers still call it the “Arctic Sea”. The Arctic Ocean is the most diverse in terms of fish species. It has a wide variety of marine species including whales, jellyfish, etc. But because of its frigid temperatures, it has little plant life. This makes it one of the most fragile ecosystems on the planet.