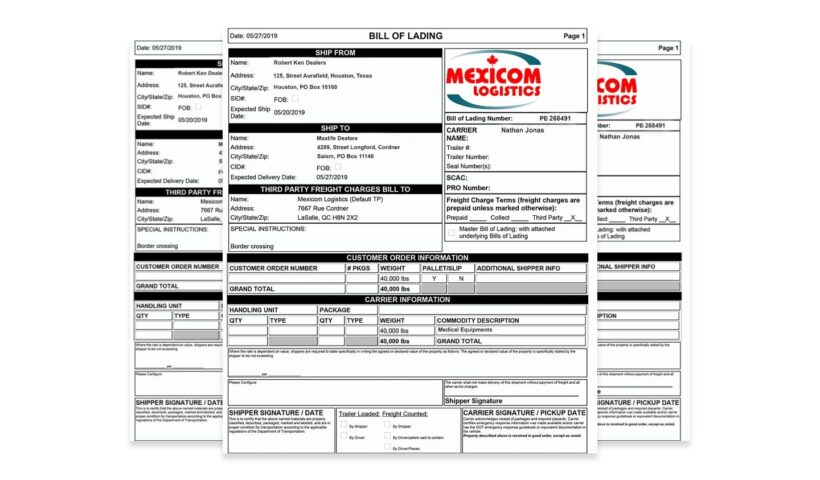
Document issued by a shipowner to a shipper of goods. It serves three purposes:
a receipt for the goods, evidence of the contract of carriage and document
of title. It contains full details of the cargo (see below).
Depending on the particular requirements of cargo interests, a number
of originals – often three – and a number of non- negotiable copies are
issued. One original bill of lading is surrendered to the carrying ship
at the discharge port or destination in exchange for the goods. Such a
bill of lading is then said to be accomplished. Once this is done, any
other original bills become non- negotiable. The copy bills of lading
are retained for reference by various parties including the shipper and
consignee.
Tag: bill of lading rules and regulations
Uniform Rules for Electronic Bills of Lading (EBL), 1990 as a International Shipping Documents
On 29 June 1990 in Paris, the CMI approved this useful document to meet the
need of uniform interpretation in the use of EBL in carriage of goods by sea. Like
any other private document, the rules shall apply whenever the parties so agree.