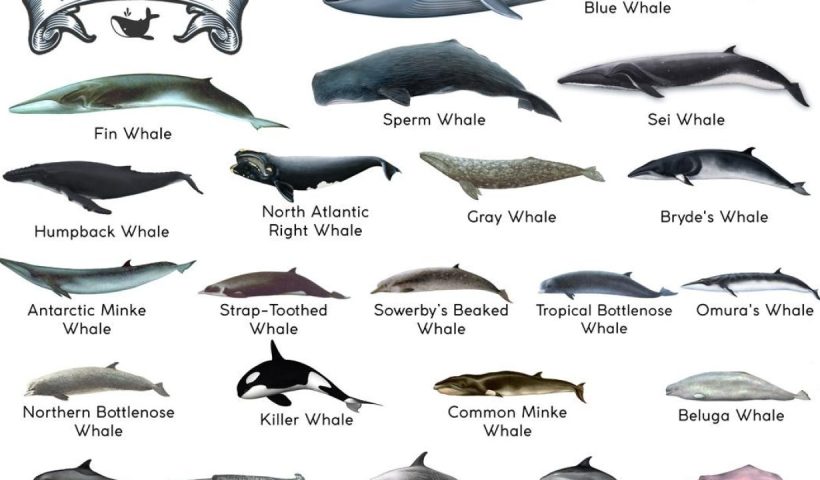
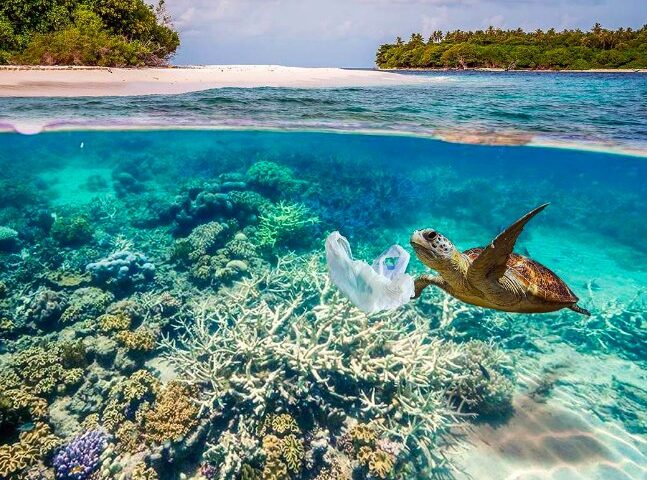
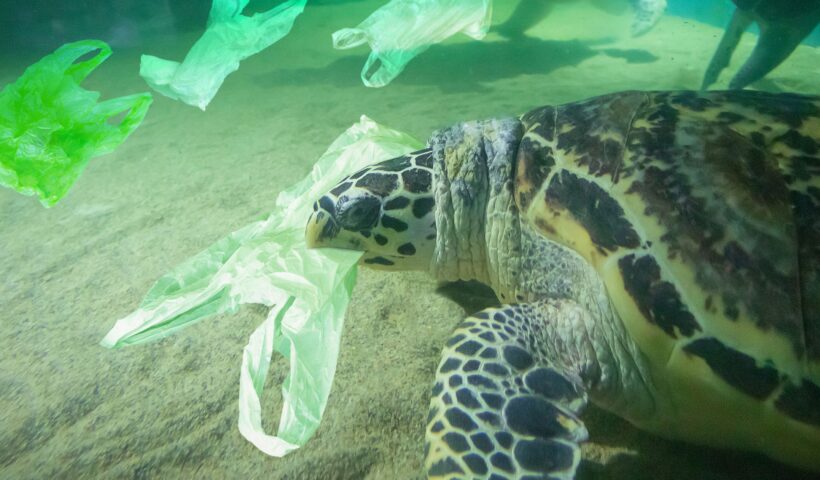
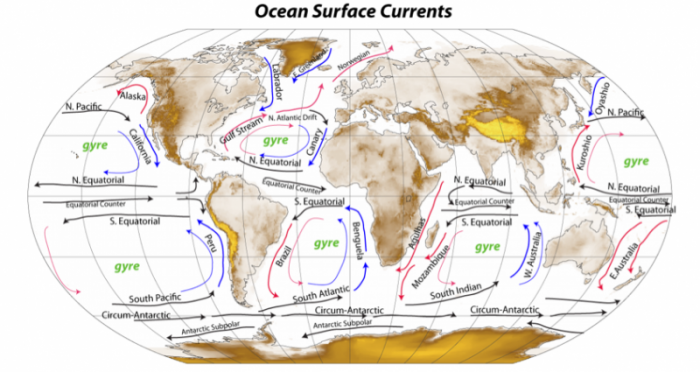
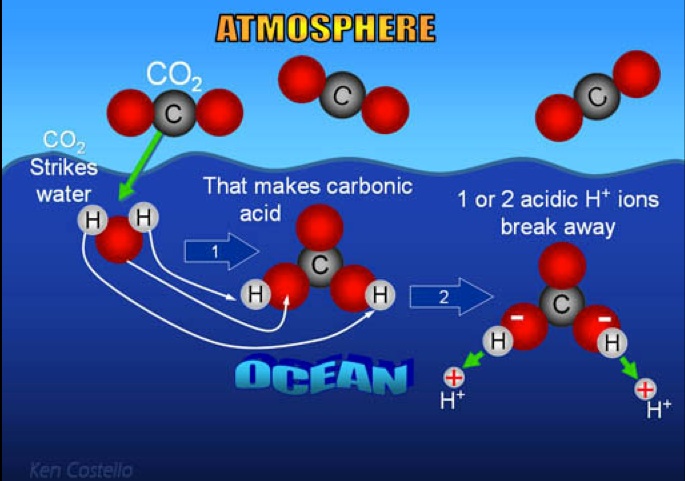
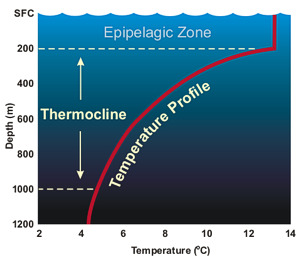
The Global Conveyor Belt, also known as the Thermohaline Circulation, is a crucial system that circulates ocean currents around the world. It plays a vital role in regulating the Earth’s climate by distributing heat and nutrients, influencing weather patterns, and transporting dissolved carbon dioxide. This intricate system of currents extends thousands of meters deep and covers vast distances, connecting all major ocean basins. Understanding the Global Conveyor Belt is essential for comprehending the complex dynamics of the oceans and the impacts it has on our planet.
View More The Global Conveyor Belt: Circulation of Ocean Currents UnveiledThe Global Conveyor Belt: Circulation of Ocean Currents Unveiled
IILSS 24th September 2023
Deep Currents: Unveiling the Hidden PathwaysEl NiñoEl Niño and La Niña: Disrupting the Conveyor BeltGlobal Conveyor BeltLa NiñaMixing and Upwelling: Essential for Oceanic BalanceMonitoring and Studying the Conveyor Belt: Methods and TechnologiesOcean Acidification: A Threat to the Global Conveyor BeltProtecting the Conveyor Belt: Ensuring a Stable Climate FutureSurface Currents: Propelling the Global Conveyor BeltThe Global Conveyor Belt: Circulation of Ocean Currents UnveiledThe Impacts of Climate Change on the Conveyor BeltThe North Atlantic Deep Water: Crucial for the Conveyor BeltThe Oceanic Circulation: A Complex and Vital Systemthermohaline circulationThermohaline Circulation: The Driving ForceUnderstanding the Global Conveyor Belt