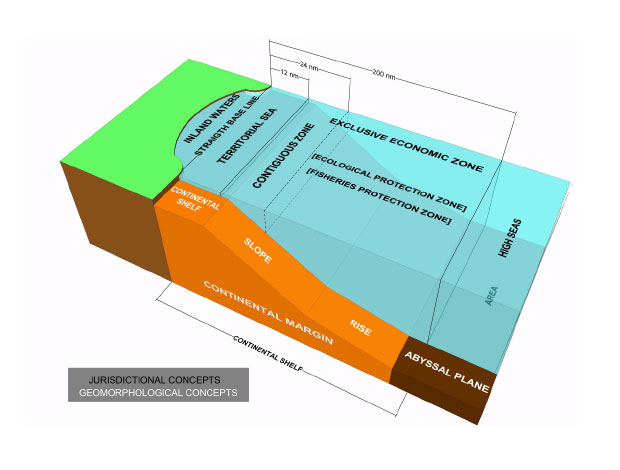
Coastal states can claim five key maritime zones. Proceeding seawards from the coast they are internal waters, territorial seas, the contiguous zone, the exclusive economic zone (or, in some cases, an exclusive fishing zone) and the continental shelf. Archipelagic states may also claim archipelagic waters within their archipelagic baselines. Beyond these national zones of jurisdiction lie the international maritime zones of the high seas and the Area.
The rights of the coastal state and aliens vary in these maritime zones, and do so both spatially and functionally. Thus, the coastal state has more rights closer to shore, for example in internal waters and the territorial sea. Aliens retain considerable rights within a coastal state’s claimed maritime zones concerned with communication issues such as navigation, overflight and the laying of submarine cables and pipelines. The coastal state, in contrast, boasts significant resource related rights, particularly concerning fishing and mineral extraction from the seabed.
Tag: delimitation of the territorial seas
TREATY LAW CONCERNING MARITIME DELIMITATION
TREATY LAW CONCERNING MARITIME DELIMITATION, 1958 Convention on the Continental Shelf, 1977 Anglo-French Continental Shelf case, continental shelf, Delimitation of the contiguous zone, delimitation of the territorial seas, determining the applicable law, EEZ, equidistance (median line), Equitable Principles, equitable solution, inequitable results, LOSC, method of delimitation, special circumstances, TSC, What are the stages of maritime boundary?, What is a single maritime boundary?, What is delimited boundary?, What is maritime space?, What is median line principle?, What is the difference between demarcation and delimitation?, Which law delimits world seas?
View More TREATY LAW CONCERNING MARITIME DELIMITATION