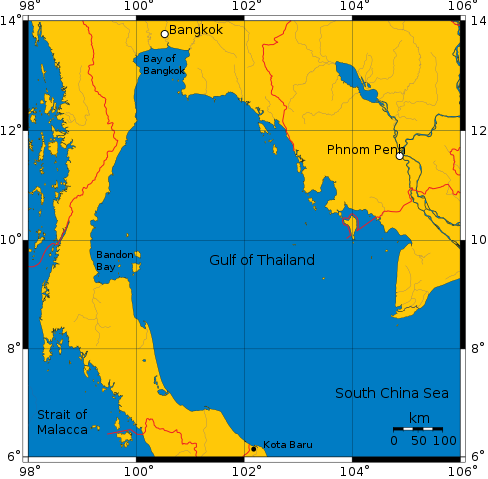
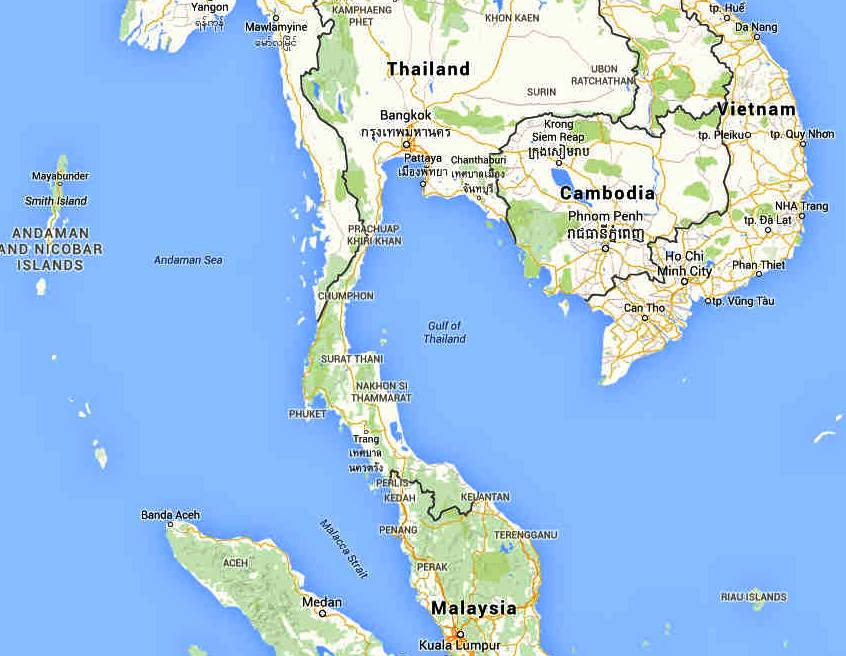
The Gulf of Thailand is a shallow inlet of the South China Sea located in the western part of the Pacific Ocean. It is surrounded by the countries of Thailand, Cambodia, and Vietnam. The gulf was formerly known as the Gulf of Siam, and in the modern Thai language, the Gulf is referred to as Ao Thai (“Thai Gulf”). The Gulf of Thailand is located in Southeast Asia immediately to the west of the South China Sea It is surrounded by Cambodia Malaysia Thailand and Vietnam The living and non living resources of the gulf are great value to the people of four littoral countries.
The Gulf of Thailand, also known as the Gulf of Siam, is a shallow inlet in the southwestern South China Sea, bounded between the southwestern shores of the Indochinese Peninsula and the northern half of the Malay Peninsula. It is around 800 km (500 mi) in length and up to 560 km (350 mi) in width, and has a surface area of 320,000 km2 (120,000 sq mi). The gulf is surrounded on the north, west and southwest by the coastlines of Thailand (hence the name), on the northeast by Cambodia and the Mekong Delta region of Vietnam, and opens to the South China Sea in the southeast.
How big is the Gulf of Thailand?
What is the Gulf famous for?
Its over fifteen thousand species of fish make it one of the most popular recreational fishing destinations in the world. There are twenty-nine species of marine mammals that call the Gulf their home including dolphins, whales, and manatees.
Are there sharks in the Gulf of Thailand?
Yes, there are nine species of shark in the Gulf of Thailand. They are: Leopard Shark. Bamboo Shark.
What 3 countries are on the Gulf of Thailand?
Gulf of Thailand, formerly Gulf Of Siam, inlet of the South China Sea bordering Thailand (southwest through north), Cambodia, and southern Vietnam (northeast).
How long before Bangkok is underwater?
Some predictions put Bangkok underwater by 2050.
Which is safest island in Thailand?
The safest places are Chiang Mai, Hua Hin, Krabi, Koh Samui, Chiang Rai, Kanchanaburi, Phang Nga, and Kuala Lumpur.
Is the Gulf of Thailand polluted?
The strong input of fresh water from the mainland makes it very susceptible to pollution from fertilizers and industrial waste, and the fishing pressure is very high.
How warm is the Gulf of Thailand? The warmest water in Gulf of Thailand was recorded today in Ban Mai. The water temperature in this location is 82°F. And the coldest in Pattaya, its value 78°F.
The modern Thai name of the gulf is Ao Thai (Thai: อ่าวไทย, ʔàːw tʰāj, ‘Thai Gulf’) and “Gulf of Thailand” has been adopted as the official name of the body by the International Hydrographic Organization.[when?] Its name in Malay is “Gulf of Siam”, Teluk Siam or in Jawi script: تلوق سيم, and in Khmer: ឈូងសមុទ្រសៀម, Chhoung Samut Siem. In Thai, the gulf is historically known as Ao Sayam (Thai: อ่าวสยาม). In Vietnamese it is known as Vịnh Thái Lan.
It is generally identified with the Great Gulf (Latin: Magnus Sinus) known to Greek, Roman, Arab, Persian, and Renaissance cartographers before the influx of Portuguese explorers removed the phantom Dragon Tail peninsula from European world maps in the 16th century.
The Gulf of Thailand is bordered by Cambodia, Thailand, Malaysia, and Vietnam. It occupies a seabed area of 304,000 km2 from 6° N to 13°30′ N latitude and 99°E to 104° E longitude.[9]: 250 The northern tip of the gulf is the Bay of Bangkok at the mouth of the Chao Phraya River. The southern boundary of the gulf is defined by a line from Cape Bai Bung in southern Vietnam (just south of the mouth of the Mekong River) to the town of Tumpat and Pengkalan Chepa on the Malaysian coast.
The gulf is relatively shallow: its mean depth is 58 metres (190 ft) and the maximum depth is only 85 metres (279 ft).: 250 This makes water exchange slow, and the strong water inflow from the rivers reduces the level of salinity in the gulf (3.05–3.25 percent) and enriches the sediments. Only at greater depths does water with a higher salinity (3.4 percent) flow into the gulf from the South China Sea. It fills the central depression below a depth of 50 metres (160 ft). The main rivers which empty into the gulf are the Chao Phraya, including its distributary Tha Chin River, the Mae Klong, and Bang Pakong rivers at the Bay of Bangkok, and to a lesser degree the Tapi River flowing into Bandon Bay in the southwest of the gulf.
The International Hydrographic Organization defines the southern limit of the gulf as “[a] line running from the Western extreme of Cambodia or Camau Point (8°36’N) to the Northern extreme of the point on the East side of the estuary of the Kelantan River (6°14′N 102°15′E)”.
